LimeMicro:LMS6002D Datasheet: Difference between revisions
Ghalfacree (talk | contribs) (Initial page creation.) |
Ghalfacree (talk | contribs) (Added remaining sections of datasheet document to page.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Serial Port Interface== | ||
The | ===Description=== | ||
The functionality of the LMS6002 transceiver is fully controlled by a set of internal registers which can be accessed through a serial port interface. Both write and read operations are supported. The serial port can be configured to run in 3 or 4 wire mode with the following pins used: | |||
* SEN - serial port enable, active low | |||
* | * SCLK - serial clock | ||
* | * SDIO - serial data in/out in 3 wire mode, serial data input in 4 wire mode | ||
* SDO-serial data out in 4 wire mode, don’t care in 3 wire mode | |||
* | |||
Serial port key features: | |||
* | * 16 serial clock cycles are required to complete write operation | ||
* | * 16 serial clock cycles are required to complete read operation | ||
* | * Multiple write/read operations are possible without toggling serial enable signal | ||
== | All configuration registers are 8-bit wide. Write/read sequence consists of 8-bit instruction followed by 8-bit data to write or read. The MSB of the instruction bit stream is used as SPI command, where CMD = 1 for write and CMD = 0 for read. Next 3 bits represent the block address, since LMS6002 configuration registers are divided into eight logical blocks as shown in the [[#Memory Map|LMS6002Dr2 Memory Map]]. The remaining 4 bits of the instruction are used to address particular registers within the block as detailed in the [[#Memory Map Description|Memory Map Description]]. Use address values from the tables. | ||
[[ | |||
Write/read cycle waveforms are shown below. Note that write operation is the same for both 3-wire and 4-wire modes. Although not shown in the figures, multiple byte write/read is possible by repeating instruction/data sequence while keeping SEN low. | |||
===Write Operation Waveform=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002D-SPI-Write-Cycle.png|center|550px|LMS6002D SPI Write Operation]] | |||
===Read Operation Waveform, 4-Wire (Default)=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002D-SPI-Read-Cycle-4-Wire.png|center|550px|LMS6002D SPI Read Operation, 4-Wire (Default)]] | |||
===Read Operation Waveform, 3-Wire=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002D-SPI-Read-Cycle-4-Wire.png|center|550px|LMS6002D SPI Read Operation, 3-Wire]] | |||
==Memory Map Description== | |||
===Memory Map=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Address (7 bits) !! Description | |||
|- | |||
| x000:xxxx || Top level configuration (as in [[#Top Level Configuration (User Mode)|Top Level Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#Top Level Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x001:xxxx || TX PLL configuration (as in [[#TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)|TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#TX/RX PLL Configuration (Test Mode)| (Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x010:xxxx || RX PLL configuration (as in [[#TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)|TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#TX/RX PLL Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x011:xxxx || TX LPF modules configuration (as in [[#TX LPF Modules Configuration (User Mode)|TX LPF Modules Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#TX LPF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x100:xxxx || TX RF modules configuration (as in [[#TX RF Modules Configuration (User Mode)|TX RF Modules Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#TX RF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x101:xxxx || RX LPF, DAC/ADC modules configuration (as in [[#RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (User Mode)|RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x110:xxxx || RX VGA2 configuration (as in [[#RX VGA2 Configuration (User Mode)|RX VGA2 Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#RX VGA2 Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|- | |||
| x111:xxxx || RX FE modules configuration (as in [[#RX FE Modules Configuration (User Mode)|RX FE Modules Configuration (User Mode)]], [[#RX FE Modules Configuration (Test Mode)|(Test Mode)]]) | |||
|} | |||
===Top Level Configuration (User Mode)=== | |||
== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits!! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x00 || 7-6 || Not used | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x01 || 7-5 || RCCAL_LPFCAL[2:0]: Value of the cal_core block in the LPF which calibrates the RC time constant. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-2 || DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register. | |||
* Locked when register value is not "000" nor "111". | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || DC_CLBR_DONE : indicates calibration status. | |||
* 1 – Calibration in progress. | |||
* 0 – Calibration is done. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR | |||
* 1 – Count Up. | |||
* 0 – Count Down. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x02 || 7-6 || Not used | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00011111 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x03 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR | |||
* 1 – Start Calibration. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Start Calibration command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR | |||
* 1 – Load Value. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Load Value command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules | |||
* 1 – Reset inactive. ('''Default''') | |||
* 0 – Reset active. | |||
|- | |||
| 2-0 || DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address. | |||
* 000 – LPF tuning module. | |||
* 001-111 – Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default''': 00001000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|0x04 || 7-4 || VER[3:0]: Chip version. | |||
|- | |||
| 3-0 || REV[3:0]: Chip revision. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
| || Default: 00100010 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="9"|0x05 || 7 || DECODE: | |||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || SRESET: DSM soft reset. | |||
* 0 – Reset state | |||
* 1 – inactive. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || EN: Top modules enable. | |||
* 0 – Top modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – Top modules enabled. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || STXEN: Soft transmit enable. | |||
* 0 – Transmitter powered down. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Transmitter enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || SRXEN: Soft receive enable. | |||
* 0 – Receiver powered down. ('''Default''') | |||
* SRXEN=1 – Receiver enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || TFWMODE: Serial port mode. | |||
* 0 – Three-wire mode. | |||
* 1 – Four-wire mode ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00110010 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x06 || 7-4 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || CLKSEL_LPFCAL: Select the clock for LPF tuning module. | |||
* 0 – 40 MHz clock generated from TX PLL output. | |||
* 1 – Use PLL reference clock. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || PD_CLKLPFCAL: Power down on-chip LPF tuning clock generation block. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. | |||
* 1 – Powered down. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || ENF_EN_CAL_LPFCAL: Enables the enforce mode. Passes FORCE_CODE_CAL_LPFCAL to RCCAL_LPFCAL. | |||
* 0 – Enforce mode disabled. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Enforce mode enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || RST_CAL_LPFCAL: Reset signal used at the beginning of calibration cycle. Reset signal needs to be longer than 100ns. | |||
* 0 – Normal state | |||
* 1 – Reset state ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00001101 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|0x07 || 7 || EN_CAL_LPFCAL: Enable signal. If =1--> the block is enabled. Should be enabled only when the RC calibration algorithm is running. | |||
* 0 – Block disabled ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Block enabled | |||
|- | |||
| 6-4 || FORCE_CODE_CAL_LPFCAL[2:0]: Input code coming from software. Will be passed to the output if ENF_EN_CAL_LPFCAL=1. | |||
* 000 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 3-0 || BWC_LPFCAL[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control. (Set this code to RXLPF BWC if RXLPF and TXLPF have different cut-off frequencies). | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! code !! Bandwidth [MHz] | |||
|- | |||
| 0000 || 14 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0001 || 10 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |0010 || 7 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0011 || 6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0100 || 5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0101 || 4.375 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0110 || 3.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |0111 || 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1000 || 2.75 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1001 || 2.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1010 || 1.92 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1011 || 1.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1100 || 1.375 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1101 || 1.25 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1110 || 0.875 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1111 || 0.75 | ||
|} | |} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x08 || 7 || Reserved. | |||
* 0 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || LBEN_LPFIN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to RXLPF input. If enabled, RXTIA should be disabled (powered down) | |||
* 0 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || LBEN_VGA2IN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to RXVGA2 input. If enabled, LPF should be disabled (powered down). | |||
* 0 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || LBEN_OPIN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to the RX output pins. If enabled, RXLPF and RXVGA2 should be disabled (powered down) | |||
* 0 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3-0 || LBRFEN[3:0]: RF loop back control. When activated, LNAs should be disabled (powered down). | |||
* 0 – RF loopback disabled '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – TXMIX output connected to LNA1 path | |||
* 2 – TXMIX output connected to LNA2 path | |||
* 3 – TXMIX output connected to LNA3 path | |||
* 4-15 – Reserved. Not valid for settings. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="10"|0x09 || 7 || RXOUTSW: RX out/ADC in high-Z switch control. | |||
* 0 – Switch open (RX output/ADC input chip pins disconnected.) '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Switch closed. RXVGA2 should be powered off first. | |||
|- | |||
| 6-0 || CLK_EN[6:0]: Clock distribution control. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6 || CLK_EN [6] | ||
* 1 – PLLCLKOUT enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – PLLCLKOUT disabled. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5 || CLK_EN [5] | ||
* 1 – LPF CAL clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – LPF CAL clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4 || CLK_EN [4] | ||
* 1 – RX VGA2 DCCAL clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – RX VGA2 DCCAL clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || CLK_EN [3] | ||
* 1 – Rx LPF DCCAL clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – Rx LPF DCCAL clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || CLK_EN [2] | ||
* 1 – RX DSM SPI clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – Rx DSM SPI clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || CLK_EN [1] | ||
* 1 – Tx LPF SPI DCCAL clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – Tx LPF SPI DCCAL clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || CLK_EN [0] | ||
* 1 – Tx DSM SPI clock enabled. | |||
* 0 – Tx DSM SPI clock disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|0x0A || 7-2 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |1 || FDDTDD: Frequency/Time division duplexing selection. | ||
* 0 – FDD mode. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – TDD mode. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || TDDMOD: TDD mode selection if FDDTDD=1. | ||
* 0 – TDD Transmit mode. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – TDD Receive mode. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|} | |||
===Top Level Configuration (Test Mode)=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="6"|0x0B || 7-5 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4 || PDXCOBUF: XCO buffer power down. | ||
* 0 – Buffer powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Buffer powered down. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || SLFBXCOBUF: XCO buffer self-biasing control. | ||
* 0 – Self-biasing disabled. | |||
* 1 – Self-biasing enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || BYPXCOBUF: XCO buffer bypass. | ||
* 0 – Buffer active. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Buffer bypassed. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1-0 || PD[1:0]: Power down control for top modules. | ||
PD[1] | |||
* 1 – PD_DCOREF_LPFCAL powered down. | |||
* 0 – PD_DCOREF_LPFCAL powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
PD[0] | |||
* 1 – RF loopback switch powered up. | |||
* 0 – RF loopback switch powered down.'''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00001000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x0E-|| 5-0 || 00000001 – v1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Read only.''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"| | |rowspan="2"|0x0F || 7-0 || SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|} | |} | ||
===TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)=== | |||
===TX | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x10, Rx: 0x20 || 7-0 || NINT[8:1]: Integer part of the divider (MSBs).* | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' ”01000001“'''0''', NINT=130. | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x11, Rx: 0x21 || 7 || NINT[0]: Integer part of the divider (LSB).* | |||
|- | |||
| 6-0 || NFRAC[22:16]: Fractional part of the divider* | |||
|- | |||
| Tx: 0x12, Rx: 0x22 || 7-0 || NFRAC[15:8] * | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x13, Rx: 0x23 || 7-0 || NFRAC[7:0] * | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' '''0'''”010…0”, NFRAC=0.25, f<sub>VCO</sub>=130.25*40MHz=5.21GHz. | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="7"|Tx: 0x14, Rx: 0x24 || 7 || DITHEN: Dithering control. | |||
* 0 – Disabled. | |||
* 1 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6-4 || DITHN[2:0]: How many bits to dither if DITHEN=1 | |||
* 000 – 1 bit. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 001 – 2 bits. | |||
* 010 – 3 bits. | |||
* … | |||
* 111 – 8 bits. | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || EN: PLL enable. | |||
* 0 – PLL powered down. | |||
* 1 – PLL enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || AUTOBYP: Delta sigma auto bypass when NFRAC = 0. | |||
* 0 – Disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Enabled | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || DECODE. | |||
* 0 – Decode power down/enable signals. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Use power down/enable signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || Reserved | |||
* 0 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “10001000” | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|Tx: 0x15, Rx: 0x25 || 7-4 || SELVCO[2:0]: VCO selection. | |||
* 000 – All VCOs powered down. | |||
* 100 – Low frequency VCO (vco4). | |||
* 101 – Mid low frequency VCO (vco3). '''(Default)''' | |||
* 110 – Mid high frequency VCO (vco2). | |||
* 111 – High frequency VCO (vco1). | |||
|- | |||
| 4-2 || FRANGE[2:0]: PLL output frequency range selection. | |||
* 000 – All dividers powered down. | |||
* 100 – Fvco/2 (2-4GHz range). '''(Default)''' | |||
* 101 – Fvco/4 (1-2GHz range). | |||
* 110 – Fvco/8 (0.5-1GHz range). | |||
* 111 – Fvco/16 (0.25-0.5GHz range). | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || SELOUT[1:0]: Select output buffer in RX PLL, not used in TX PLL. | |||
* 00 – All output buffers powered down. | |||
* 01 – First buffer enabled for LNA1 path. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 10 – Second buffer enabled for LNA2 path. | |||
* 11 – Third buffer enabled for LNA3 path. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “10110001” | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|Tx: 0x16, Rx: 0x26 || 7 || EN_PFD_UP: Enable PFD UP pulses. | |||
* 0 – Disabled. | |||
* 1 –Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || OEN_TSTD_SX. | |||
* 0 – Test signal output buffer disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Test signal output buffer enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || PASSEN_TSTOD_SD. | |||
* 0 – Test signal pass disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Test signal pass enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-0 || CHP[4:0]: Charge pump current. Binary coded, LSB = 100uA. | |||
* 00000 – 0uA. | |||
* 00001 – 100uA. | |||
* ... | |||
* 11000 – 2400uA. | |||
* ... – 2400uA. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “10001100”, ICHP = 1.2mA | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|Tx: 0x17, Rx: 0x27 || 7 || BYPVCOREG: Bypass VCO regulator. | |||
* 0 – Not bypassed. | |||
* 1 – Regulator bypassed. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || PDVCOREG: VCO regulator power down. | |||
* 0 – Regulator powered up. | |||
* 1 – Regulator powered down. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || FSTVCOBG: VCO regulator band gap settling time control. Shorts the resistor in band gap to speed up charging for faster response. After the initial charge up, it should be disabled. | |||
* 1 – Resistor shorted. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Switch open. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-0 || OFFUP[4:0]: Charge pump UP offset current. Binary coded, LSB = 10uA. | |||
* 00000 – 0uA. | |||
* 00001 – 10uA. | |||
* ... | |||
* 11000 – 240uA. | |||
* ... – 240uA. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “11100000” = 0mA. | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|Tx: 0x18, Rx: 0x28 || 7-5 || VOVCOREG[3:1]: VCO regulator output voltage control, 3 MSBs. LSB=100mV, VOVCOREG[3:0] coded as below. | |||
* 0000 – 1.4V, min output. | |||
* ... | |||
* 0101 – 1.9V. '''(Default)''' | |||
* ... | |||
* 1100 – 2.6V, max output. | |||
* 1101, 1110, 1111 – not valid codes | |||
|- | |||
| 4-0 || OFFDOWN[4:0]: Charge pump DOWN offset current. Binary coded, LSB = 10uA. | |||
* 00000 – 0uA. | |||
* 00001 – 10uA. | |||
* ... | |||
* 11000 – 240uA. | |||
* ... – 240uA. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' “01000000” = 0mA. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|Tx: 0x19, Rx: 0x29 || 7 || VOVCOREG[0]: VCO regulator output voltage control, LSB. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-0 || VCOCAP[5:0]: Switch capacitance programming. Binary coded. | ||
* 000000 – Max capacitance, min frequency. | |||
* 010100 – '''(Default)''' | |||
* 111111 – Min capacitance, max frequency. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' “10010100", VCOCAP=20 | ||
|} | |} | ||
* Shadow registered | |||
===RX | ===TX/RX PLL Configuration (Test Mode)=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|Tx: 0x1A, Rx: 0x2A || 7 || VTUNE_H ('''Read Only'''): Value from Vtune comparator. | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || VTUNE_L ('''Read Only'''): Value from Vtune comparator. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || Reserved | |||
* 000011 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “00000011” | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|Tx: 0x1B, Rx: 0x2B || 7-4 || Reserved | |||
* 0111 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || PD_VCOCOMP_SX: VCO Comparator enable. | |||
* 0 – Enabled (powered up). '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – disabled (powered down). | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || Reserved. | |||
* 1 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || Reserved. | |||
* 1 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || Reserved. | |||
* 1 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “01110110”, A value = 0, (N=130). | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x1C, Rx: 0x2C || 7-0 || Reserved. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' “00111000” | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x1D, Rx: 0x2D || 7-0 || Reserved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Read only.''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x1E, Rx: 0x2E || 7-0 || Reserved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Read only.''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|Tx: 0x1F, Rx: 0x2F || 7-0 || Reserved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Read only.''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | ===TX LPF Modules Configuration (User Mode)=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x30 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x31 || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-2 || DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register. | |||
* Locked, when register value is neither "000" nor "111". | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || DC_CLBR_DONE: indicates calibration status. | |||
* 1 – Calibration in progress. | |||
* 0 – Calibration is done. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Count Up. | |||
* 0 – Count Down. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x32 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_CNTVAL[5:0]: Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00011111 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x33 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5 || DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of module selected by DC_ADDR. | ||
* 1 – Start calibration. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate start calibration command. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4 || DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR. | ||
* 1 – Load Value. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Load Value command. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || DC_SRESET: Resets all DC Calibration modules. | ||
* 1 – Reset inactive. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Reset active. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2-0 || DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address. | ||
* 000 – I filter. | |||
* 001 – Q filter. | |||
* 010 – 111 Not used. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00001000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="5"|0x34 || 7-6 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style=" | | 5-2 || BWC_LPF[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! code !! Bandwidth [MHz] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0000 || 14 ('''Default''') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0001 || 10 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |0010 || 7 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0011 || 6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0100 || 5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0101 || 4.375 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0110 || 3.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |0111 || 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1000 || 2.75 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1001 || 2.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1010 || 1.92 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1011 || 1.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|1. | | 1100 || 1.375 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1101 || 1.25 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1110 || 0.875 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1111 || 0.75 | ||
|} | |} | ||
|- | |||
| 1 || EN : LPF modules enable. | |||
* 0 – LPF modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – LPF modules enabled. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DECODE. | |||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000010 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|0x35 | |||
DCO_DACCAL_LPF renamed, no action required. | |||
| 7 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || BYP_EN_LPF: LPF bypass enable. | |||
* 1 – Bypass switches will bypass the LPF. | |||
* 0 – Normal operation. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DCO_DACCAL[5:0]: Resistor calibration control for the DC offset cancellation DAC. | |||
* 001100 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00001100 | |||
|} | |||
* | |||
===TX LPF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)=== | |||
=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="7"|0x36 || 7 || TX_DACBUF_PD: TX data DAC buffers power down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
|- | |||
| 6-4 || RCCAL_LPF[2:0]: Calibration value, coming from TRX_LPF_CAL module. | |||
* 011 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || PD_DCODAC_LPF: Power down for the DAC in the DC offset cancellation block. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || PD_DCOREF_LPF: Power down signal for the dc_ref_con3 block. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || PD_FIL_LPF: Power down for the filter. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00110000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|0x3E || 7-0 || SPARE0[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x3F || 7 || PD_DCOCMP_LPF: Power down DC offset comparators in DC offset cancellation block. Should be powered up only when DC offset cancellation algorithm is running. | ||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || SPARE1[6:0]: Spare configuration register | ||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (User Mode)=== | ||
( | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x50 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC Calibration module, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x51 || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-2 || DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register. | |||
* Locked, when register value is neither "000" nor "111". | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || DC_CLBR_DONE: indicates calibration status. | |||
* 1 – Calibration in progress. | |||
* 0 – Calibration is done. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Count Up. | |||
* 0 – Count Down. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x52 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00011111 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x53 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Start Calibration. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Start Calibration command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Load Value. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Load Value command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules. | |||
* 1 – Reset inactive. ('''Default''') | |||
* 0 – Reset active. | |||
|- | |||
| 2-0 || DC_ADDR[3:0]: Active calibration module address. | |||
* 000 – I filter. ('''Default''') | |||
* 001 – Q filter. | |||
* 010-111 – Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00001000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x54 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-2 || BWC_LPF[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! code !! Bandwidth [MHz] | |||
|- | |||
| 0000 || 14 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 0001 || 10 | |||
|- | |||
|0010 || 7 | |||
|- | |||
| 0011 || 6 | |||
|- | |||
| 0100 || 5 | |||
|- | |||
| 0101 || 4.375 | |||
|- | |||
| 0110 || 3.5 | |||
|- | |||
|0111 || 3 | |||
|- | |||
| 1000 || 2.75 | |||
|- | |||
| 1001 || 2.5 | |||
|- | |||
| 1010 || 1.92 | |||
|- | |||
| 1011 || 1.5 | |||
|- | |||
| 1100 || 1.375 | |||
|- | |||
| 1101 || 1.25 | |||
|- | |||
| 1110 || 0.875 | |||
|- | |||
| 1111 || 0.75 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || EN : LPF modules enable. | |||
* 0 – LPF modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – LPF modules enabled. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DECODE. | |||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000010 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|0x55 || 7 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || BYP_EN_LPF: LPF bypass enable. | |||
* 1 – Bypass switches will bypass the LPF. | |||
* 0 – Normal operation. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DCO_DACCAL[5:0]: Resistor calibration control for the DC offset cancellation DAC. | |||
* 001100 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00001100 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="7"|0x56 || 7 || TX_DACBUF_PD: Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 6-4 || RCCAL_LPF[2:0]: Calibration value, coming from TRX_LPF_CAL module. | |||
* 011 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || PD_DCODAC_LPF: Power down for the DAC in the DC offset cancellation block. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || PD_DCOREF_LPF: Power down signal for the dc_ref_con3 block. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || PD_FIL_LPF: Power down for the filter. | |||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00110000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x57 || 7 || EN_ADC_DAC : ADC/DAC modules enable. | |||
* 0 – ADC/DAC modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – ADC/DAC modules enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || DECODE. | |||
* 0 – Decode ADC/DAC enable signals. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Use ADC/DAC enable signals from MISC_CTRL[4:0] register. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-3 || TX_CTRL1[6:4]. DAC Internal Output Load Resistor Control Bits. | |||
* 111 – 50 Ohms. | |||
* 110 – 100 Ohms. | |||
* 101 – 66 Ohms. | |||
* 100 – 200 Ohms. | |||
* 011 – 66 Ohms. | |||
* 010 – 200 Ohms. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 001 – 100 Ohms. | |||
* 000 – Open Circuit. | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || TX_CTRL1[3]. DAC Reference Current Resistor. | |||
* 1 – External. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Internal. | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || TX_CTRL1[1:0]. DAC Full Scale Output Current Control (single-ended). | |||
* 11 – Iout FS=5ma. | |||
* 10 – Iout FS=2.5ma. | |||
* 01 – Iout FS=10ma. | |||
* 00 – Iout FS=5ma. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 10010100 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4"|0x58 || 7-6 || RX_CTRL1[7:6]. Reference bias resistor adjust. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5-4 || RX_CTRL1[5:4]. Reference bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 2.5X. | |||
* 10 – 2.0X. | |||
* 01 – 1.5X. | |||
* 00 – 1.0X. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3-0 || RX_CTRL1[3:0]. Reference bias DOWN. | |||
* 1111 – Min bias. | |||
* … | |||
* 0000 – Max bias. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x59 || 7 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 6-5 || RX_CTRL2[7:6]. Reference Gain Adjust. | |||
* 11 – 1.25V. | |||
* 10 – 1.00V. | |||
* 01 – 1.75V. | |||
* 00 – 1.50V. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 4-3 || RX_CTRL2[5:4]. Common Mode Adjust. | |||
* 11 – 790mV | |||
* 10 – 700mV | |||
* 01 – 960mV | |||
* 00 – 875mV '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 2-1 || RX_CTRL2[3:2]. Reference Buffer Boost. | |||
* 11 – 2.5X. | |||
* 10 – 2.0X. | |||
* 01 – 1.5X. | |||
* 00 – 1.0X. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || RX_CTRL2[0]. ADC Input Buffer Disable. | |||
* 1 – Disabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Enabled. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000001 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="8"|0x5A || 7 || MISC_CTRL[9]. Rx Fsync Polarity, frame start. | |||
* 1 – 1. | |||
* 0 – 0. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 6 || MISC_CTRL[8]. Rx Interleave Mode. | |||
* 1 – Q,I. | |||
* 0 – I,Q. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || MISC_CTRL[7]. DAC Clk Edge Polarity. | |||
* 1 – Negative. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Positive. | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || MISC_CTRL[6]. Tx Fsync Polarity, frame start. | |||
* 1 – 1. | |||
* 0 – 0. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || MISC_CTRL[5]. Tx Interleave Mode. | |||
* 1 – Q,I. | |||
* 0 – I,Q. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || RX_CTRL3[7]. ADC Sampling Phase Select. | |||
* 1 – Falling edge. | |||
* 0 – Rising edge. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || RX_CTRL3[1:0]. Clock Non-Overlap Adjust. | |||
* 11 – +300ps. | |||
* 10 – +150ps. | |||
* 01 – +450ps. | |||
* 00 – Nominal. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00100000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x5B || 7-6 || RX_CTRL4[7:6] ADC bias resistor adjust. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5-4 || RX_CTRL4[5:4]. Main bias DOWN. | |||
* 11 – Min bias. | |||
* 10 – | |||
* 01 – | |||
* 00 – Nominal. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3-2 || RX_CTRL4[3:2]. ADC Amp1 stage1 bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || RX_CTRL4[1:0]. ADC Amp2-4 stage1 bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x5C || 7-6 || RX_CTRL5[7:6] ADC Amp1 stage2 bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 5-4 || RX_CTRL5[5:4]. ADC Amp2-4 stage2 bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3-2 || RX_CTRL5[3:2]. Quantizer bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || RX_CTRL5[1:0]. Input Buffer bias UP. | |||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x5D || 7-4 || REF_CTRL0[7:4]. Bandgap Temperature Coefficient Control. | ||
* 0111 – Max. | |||
* 0000 – Nominal. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1000 – Min. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || REF_CTRL0[3:0]. Bandgap Gain Control. | ||
* 0111 – Max. | |||
* 0000 – Nominal. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1000 – Min. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|0x5E || 7-6 || REF_CTRL1[7:6]. Reference Amps bias adjust. | ||
* 11 – 15uA. | |||
* 10 – 10uA. | |||
* 01 – 40uA. | |||
* 00 – 20uA. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-4 || REF_CTRL1[5:4]. Reference Amps bias UP. | ||
* 11 – 2.5X. | |||
* 10 – 2.0X. | |||
* 01 – 1.5X. | |||
* 00 – 1.0X. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || REF_CTRL1[3:0]. Reference Amps bias DOWN. | ||
* 1111 – Min bias. | |||
* … | |||
* 0000 – Max bias. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (Test Mode)=== | ||
( | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="8"|0X5F || 7 || PD_DCOCMP_LPF: Power down DC offset comparators in DC offset cancellation block. Should be powered up only when DC offset cancellation algorithm is running. | ||
* 1 – Powered Down. | |||
* 0 – Enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-5 || SPARE00[6:5]: Spare configuration bits. | ||
* 00 – '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4 || MISC_CTRL[4]. Enable DAC. | ||
* 1 – Enable. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Off. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || MISC_CTRL[3]. Enable ADC1 (I Channel). | ||
* 1 – Enable. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Off. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || MISC_CTRL[2]. Enable ADC2 (Q Channel). | ||
* 1 – Enable. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Off. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || MISC_CTRL[1]. Enable ADC reference. | ||
* 1 – Enable. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Off. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || MISC_CTRL[0]. Enable master reference. | ||
* 1 – Enable. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 0 – Off. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00011111 | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===TX RF Modules Configuration (User Mode)=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x40 || 7-2 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || EN : TXRF modules enable | |||
* 0 – TXRF modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – TXRF modules enabled. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DECODE: | |||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x41 || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-0 || VGA1GAIN[4:0]: TXVGA1 gain, log-linear control. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |||
| 00000 || -35 | |||
|- | |||
| 00001 || -34 | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
| 10101 || -14 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
| 11110 || -5 | |||
|- | |||
| 11111 || -4 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00010101 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|0x42 || 7-0 || VGA1DC_I[7:0]: TXVGA1 DC shift control, LO leakage cancellation. LSB=0.0625mV, encoded as shown below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! DC Shift [mV] | |||
|- | |||
| 00000000 || -16 | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
|01111111 || -0.0625 | |||
|- | |||
| 10000000 || 0 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 10000001 || 0.0625 | |||
|- | |||
| … | |||
|- | |||
| 11111111 || 15.9375 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 10000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|0x43 || 7-0 || VGA1DC_Q[7:0]: TXVGA1 DC shift control, LO leakage cancellation LSB=0.0625mV, encoded as shown below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! DC Shift [mV] | |||
|- | |||
| 00000000 || -16 | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
|01111111 || -0.0625 | |||
|- | |||
| 10000000 || 0 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 10000001 || 0.0625 | |||
|- | |||
| … | |||
|- | |||
| 11111111 || 15.9375 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 10000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x44 || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-3 || PA_EN[2:0]: VGA2 power amplifier (TX output) selection. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! PA_EN{2:1] !! PA1 !! PA2 | |||
|- | |||
| 00 || OFF || OFF | |||
|- | |||
| 01 || ON || OFF ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 10 || OFF || ON | |||
|- | |||
| 11 || OFF || OFF | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || PA_EN[2]: AUXPA, auxiliary (RF loopack) PA power down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
|- | |||
| 1-0 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00001011 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x45 || 7-3 || VGA2GAIN[4:0]: TXVGA2 gain control, log-linear control. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |||
| 00000 || 0 '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 00001 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| 11001 || 25 ... | |||
|- | |||
| 11111 || 25 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| 2-0 || ENVD[2:0]: Controls envelop/peak detector analogue MUX. | |||
* ENVD[2]: Selects the signal for AC coupling, MUX provides: | |||
** 0 – Reference DC generated inside the selected detector. '''(Default)''' | |||
** 1 – Average of the selected detector output. | |||
* ENVD[1:0]: Detector select, MUX provides | |||
** 00 – AUXPA envelop detector output '''(Default)''' | |||
** 01 – AUXPA peak detector output. | |||
** 10 – PA1 envelop detector output. | |||
** 11 – PA2 envelop detector output. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x46 || 7-4 || PKDBW[3:0]: Controls the bandwidth of the envelop and peak detectors. | |||
* 0000 – Minimum bandwidth, envelop ~1MHz, peak 30kHz. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1111 – Maximum bandwidth, envelop ~15MHz, peak ~300KHz. | |||
|- | |||
| 3-2 || LOOPBBEN[1:0]: Base band loopback switches control. | |||
* 00 – Switch open. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 11 – Switch closed. | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || FST_PKDET: Shorts the resistor in the envelop/peak detector to speed up charging for faster response. After the initial charge up, it should be disabled to achieve a LPF function. | |||
* 0 – Switch open, LPF function in effect. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Resistor shorted (no LPF function). | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || FST_TXHFBIAS: Bias stage of high frequency TX part has large resistors to filter the noise. However, they create large settling time. This switch can be used to short those resistors during the initialization and then it may be needed to open it to filter the noise, in case the noise is too high. | |||
* 0 – Switch open (noise filtering functional). '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Resistors shorted (short settling - no noise filtering). | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x47 || 7-4 || ICT_TXLOBUF[3:0]: Controls the bias current of the LO buffer. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=5/6mA. | |||
* 0000 – Minimum current. | |||
* 0110 – TXMIX takes 5mA for buffer. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1111 – Maximum current. | |||
|- | |||
| 3-0 || VBCAS_TXDRV[3:0]: The linearity of PAs depends on the bias at the base of the cascode NPNs in the PA cells. Increasing the VBCAS will lower the base of the cascode NPN. | |||
* 0000 – Maximum base voltage. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1111 – Minimum base voltage. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01100000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x48 || 7-5 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4-0 || ICT_TXMIX[4:0]: Controls the bias current of the mixer. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=1mA. | ||
* 00000 – 0mA. | |||
* 01100 – TXMIX takes 12mA for each cell. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 11111 – 31mA. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || Default: 00001100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x49 || 7-5 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4-0 || ICT_TXDRV[4:0]: Controls the bias current of the PAs. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=1mA. | ||
* 00000 – 0mA. | |||
* 01100 – PAs take 12mA for each cell. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 11111 – 31mA. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || Default: 00001100 | ||
|} | |} | ||
===TX RF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! Address (7 bits) !! Description | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="7"|0x4A || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || PW_VGA1_I: VGA1, I channel power control. | |||
* 0 – Powered down. | |||
* 1 – Powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || PW_VGA1_Q: VGA1, Q channel power control. | |||
* 0 – Powered down. | |||
* 1 – Powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || PD_TXDRV: Power down for PAs and AUXPA. | |||
* 0 – PA1, PA2 and AUXPA can be separately controlled. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – PA1, PA2 and AUXPA all disabled | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || PD_TXLOBUF: Power down for TXLOBUF. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || PD_TXMIX: Power down for TXMIX. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00011000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="2"|0x4B || 7-0 || VGA1GAINT[7:0]: TXVGA1 gain control, raw access. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |||
| 00000 || -35 | |||
|- | |||
| 00001 || -34 | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
| 10101 || -14 '''(Default)''' | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
| 11110 || -5 | |||
|- | |||
| 11111 || -4 | |||
|} | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01010000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x4C || 7-0 || G_TXVGA2[8:1]: Controls the gain of PA1, PA2 and AUXPA, raw access. | ||
* For PA1, PA2: <math>\mathrm{Gain} = 20 * \log 10 \left( 0.038 * \mathit{G\_TXVGA2[8:0]} \right)</math>. | |||
* For AUXPA: Only 4 LSBs are used, max gain ~22dB. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000, 0dB gain. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x4D || 7 || PD_PKDET: Power down for envelop/peak detectors. | ||
* 0 – Powered up. '''(Default)''' | |||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || SPARE0[6:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x4F || 7-0 || SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || Default: 00000000 | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===RX VGA2 Configuration (User Mode)=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | ||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x60 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC Calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read Only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x61 || 7-5 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 4-2 || DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register. | |||
* Locked when register value is not "000" nor "111". | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || DC_CLBR_DONE : indicates calibration status. | |||
* 1 – Calibration in progress. | |||
* 0 – Calibration is done. | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR | |||
* 1 – Count Up. | |||
* 0 – Count Down. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Read only.''' | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="3"|0x62 || 7-6 || Not used | |||
|- | |||
| 5-0 || DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00011111 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="6"|0x63 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Start Calibration. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Start Calibration command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR. | |||
* 1 – Load Value. | |||
* 0 – Deactivate Load Value command. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules. | |||
* 1 – Reset inactive. ('''Default''') | |||
* 0 – Reset active. | |||
|- | |||
| 2-0 || DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address. | |||
* 000 – DC reference module. | |||
* 001 – First gain stage (VGA2A), I channel. | |||
* 010 – First gain stage (VGA2A), Q channel. | |||
* 011 – Second gain stage (VGA2B), I channel. | |||
* 100 – Second gain stage (VGA2B), Q channel. | |||
* 101-111 – Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default''': 00001000 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="5"|0x64 || 7-6 || Not used. | |||
|- | |||
| 5-2 || VCM[3:0]: RXVGA2 output common mode voltage control. VCM[3] – sign, VCM[2:0] – magnitude, LSB=40mV. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Voltage [V] | |||
|- | |||
| 0000 || 1.18 | |||
|- | |||
| 0001 || 1.14 | |||
|- | |||
| 0010 || 1.10 | |||
|- | |||
| 0011 || 1.06 | |||
|- | |||
| 0100 || 1.02 | |||
|- | |||
| 0101 || 0.98 | |||
|- | |||
| 0110 || 0.94 | |||
|- | |||
| 0111 ||0.90 ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |||
| 1000 || 0.62 | |||
|- | |||
| 1001 || 0.66 | |||
|- | |||
| 1010 || 0.70 | |||
|- | |||
| 1011 || 0.74 | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1100 || 0.78 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1101 || 0.82 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1110 || 0.86 | ||
|} | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || EN :RXVGA2 modules enable. | ||
* 0 – RXVGA2 modules powered down. | |||
* 1 – RXVGA2 modules enabled. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || DECODE: | ||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00011110 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x65 || 7-5 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4-0 || VGA2GAIN[4:0]: RXVGA2 gain control. LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 00000 || 0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 00001 || 3 ('''Default''') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | … || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 01001 || 27 | ||
|- | |||
| 01010 || 30 | |||
|- | |||
| … || | |||
|- | |||
| 10100 || 60 | |||
|} | |||
Not recommended to be used above 30dB. | |||
|- | |||
| || '''Default:''' 00000001 | |||
|} | |||
===RX VGA2 Configuration (Test Mode)=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="9"|0x66 || || PD[9:0]: Power down different modules. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 7-6 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5 || PD[9] - DC current regulator. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4 || PD[8] - DC calibration DAC for VGA2B. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || PD[6] - DC calibration DAC for VGA2A. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || PD[4] - Band gap. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="6"|0x67 || 7-4 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || PD[3] – Output buffer in both RXVGAs. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || PD[2] - RXVGA2B. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || PD[1] - RXVGA2A. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || PD[0] - Current reference. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x68 || 7-4 || VGA2GAINB: Controls the gain of second VGA2 stage (VGA2B). LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0000 || 0 ('''Default''') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0001 || 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | … || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1001 || 27 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1010 || 30 | ||
|} | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || VGA2GAINA: Controls the gain of first VGA2 stage (VGA2A). LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 50px; margin-left: right;" | |||
! Code !! Gain [dB] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0000 || 0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0001 || 3 ('''Default''') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | … || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1001 || 27 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1010 || 30 | ||
|} | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000001 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|0x6E || 7 || PD[7] - DC calibration comparator for VGA2B. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6 || PD[6] - DC calibration comparator for VGA2A. | ||
* 1 – Powered down. | |||
* 0 – Powered up. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-0 || SPARE0[5:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x6F || 7-0 || SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|} | |||
===RX FE Modules Configuration (User Mode)=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|0x70 || 7-2 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || DECODE. | ||
* 0 – Decode control signals. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Use control signals from test mode registers. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || EN: RXFE modules enable. | ||
* 0 – Top modules powered down | |||
* 1 – Top modules enabled ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000001 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x71 || 7 || IN1SEL_MIX_RXFE: Selects the input to the mixer. | ||
* 1 – Input 1 is selected, shorted on-chip to LNA internal output. ('''Default''') | |||
* 0 – Input 2 is selected, connected to pads. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || DCOFF_I_RXFE[6:0]: DC offset cancellation, I channel. | ||
* Code is Sign(<6>)-Magnitude(<5:0>), signed magnitude format. | |||
* 0000000 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 10000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x72 || 7 || INLOAD_LNA_RXFE: To select the internal load for the LNA. | ||
* 1 – Internal load is active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 0 – Internal node is disabled. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || DCOFF_Q_RXFE[6:0]: DC offset cancellation, Q channel. | ||
* Code is Sign(<6>)-Magnitude(<5:0>), signed magnitude format. | |||
* 0000000 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 10000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x73 || 7 || XLOAD_LNA_RXFE: To select the externa load for the LNA. | ||
* 1 – External load is active. | |||
* 0 – External node is disabled. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || IP2TRIM_I_RXFE[6:0]: IP2 cancellation, I channel. | ||
* Code is Sign(<6>)-Magnitude(<5:0>), signed magnitude format. | |||
* 0000000 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="4"|0x75 || 7-6 || G_LNA_RXFE[1:0]: LNA gain mode control. | ||
* 11 – Max gain (all LNAs). ('''Default''') | |||
* 10 – Mid gain (all LNAs). | |||
* 01 – LNA bypassed (LNA1 and LNA2). | |||
* 00 – Max gain (LNA3). | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-4 || LNASEL_RXFE[1:0]: Selects the active LNA. | ||
* 00 – All LNAs disabled. | |||
* 01 – LNA1 active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 10 – LNA2 active. | |||
* 11 – LNA3 active. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || CBE_LNA_RXFE[3:0]: Controls the capacitance parallel to the BE of the input NPN transistors. To be used at lower frequencies for easier matching. For LNA1 and LNA2 only. | ||
* 0000 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 11010000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x76 || 7 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || RFB_TIA_RXFE[6:0]: Feedback resistor control of the TIA (RXVGA1) to set the mixer gain. | ||
* If = 120 --> mixer gain = 30dB ('''Default''') | |||
* If = 102 --> mixer gain = 19dB | |||
* If = 2 --> mixer gain = 5dB | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01111000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x77 || 7 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-0 || CFB_TIA_RXFE[6:0]: Feedback capacitor for the TIA (RXVGA1) to limit the BW. | ||
* If = 0, min cap --> BW~45MHz for gain of 30dB. ('''Default''') | |||
* If = 19 --> BW=2.5MHz for MixGain=30dB and at TT. | |||
This cap is supposed to be set according to the RC time constant to have almost constant BW over the corners for optimum CDMA performance. Software will control it using the information from the LPF calibration circuit. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x78 || 7-6 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-0 || RDLEXT_LNA_RXFE[5:0]: Controls the on-chip LNA load resistor for the external load mode of the LNA. In practice, this will be set to high value, the output will be ac coupled, and the actual load is defined on PCB. | ||
* 011100 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00011100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x79 || 7-6 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5-0 || RDLINT_LNA_RXFE[5:0]: Controls the on-chip LNA load resistor for the internal load mode of the LNA, LNA1 and LNA2. | ||
* 011100 – ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00011100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x7A || 7-4 || ICT_MIX_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for mixer. | ||
* 0000 - 0 bias current. | |||
* 0111 - nominal bias current. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1111 - 2.1x nominal bias current. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || ICT_LNA_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for LNA. | ||
* 0000 - 0 bias current. | |||
* 0111 - nominal bias current. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1111 - 2.1x nominal bias current. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01110111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="3"|0x7B || 7-4 || ICT_TIA_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for TIA (RXVGA1). | ||
* 0000 - 0 bias current. | |||
* 0111 - nominal bias current. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1111 - 2.1x nominal bias current. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3-0 || ICT_MXLOB_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for mixer LO buffer. | ||
* 0000 - 0 bias current. | |||
* 0111 - nominal bias current. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1111 - 2.1x nominal bias current. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 01110111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="5"|0x7C || 7 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 6-3 || LOBN_MIX_RXFE[3:0]: Tweak for the LO bias of the mixer for optimum linearity. | ||
* 0000 – Minimum bias voltage. | |||
* 0011 – ('''Default''') | |||
* 1111 – Maximum bias voltage. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || RINEN_MIX_RXFE: Termination resistor on external mixer input enable. | ||
* 1 – Active. | |||
* 0 – Inactive. ('''Default''') | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1-0 || G_FINE_LNA3_RXFE[1:0]: LNA3 fine gain adjustment. | ||
* 00 – +0 dB ('''Default''') | |||
* 01 – +1 dB | |||
* 10 – +2 dB | |||
* 11 – +3 dB | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00011000 | ||
|} | |||
===RX FE Modules Configuration (Test Mode)=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Address (7 bits) !! Bits !! Description | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="6"|0x7D || 7-4 || Not used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3 || PD_TIA_RXFE: TIA (RXVGA1) power down. | ||
* 0 – Block active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Block inactive. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || PD_MXLOB_RXFE: Mixer LO buffer power down. | ||
* 0 – Block active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Block inactive. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || PD_MIX_RXFE: Mixer power down. | ||
* 0 – Block active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Block inactive. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || PD_LNA_RXFE: LNA power down. | ||
* 0 – Block active. ('''Default''') | |||
* 1 – Block inactive. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x7E || 7-0 || SPARE0[7:0] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |rowspan="2"|0x7F || 7-0 || SPARE1[7:0] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | || '''Default:''' 00000000 | ||
|} | |||
==Control Block Diagrams== | |||
===SPI Read/Write Pseudocode=== | |||
<source lang="c"> | |||
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
// Write command, SPI module address, register address | |||
// Read data | |||
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
void SPI_Read(BYTE COMMAND) | |||
{ | |||
BYTE DATA; //We will read data there | |||
//Write Command and Address (MSB First) | |||
//First 1 bit (MSB) = Command | |||
//Next 3 bits = SPI memory block address | |||
//Next 4 (LSBs) bits = Register Address | |||
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--) | |||
{ | |||
if(i’th bit in COMMAND is ‘1’) | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘1’; | |||
} | |||
else | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘0’; | |||
}; | |||
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line; | |||
}; | |||
//Read Data (MSB First) | |||
//Note: At this point we have data MSB valid from the chip. | |||
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--) | |||
{ | |||
if(there is ‘1’ at the Data Input Line) | |||
{ | |||
Set i’th bit in DATA ‘1’; | |||
} | |||
else | |||
{ | |||
Set i’th bit in DATA ‘0’; | |||
}; | |||
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
// Write data to the chip: | |||
// First byte: Command, SPI module address, register address | |||
// Second byte: Data | |||
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
void SPI_Write(BYTE COMMAND, BYTE DATA) | |||
{ | |||
//Write Command, Address | |||
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--) | |||
{ | |||
if(i’th bit in COMMAND is ‘1’) | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘1’; | |||
} | |||
else | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘0’; | |||
}; | |||
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line; | |||
}; | |||
//Write Data | |||
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--) | |||
{ | |||
if(i’th bit in DATA is ‘1’) | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘1’; | |||
} | |||
else | |||
{ | |||
Set Data Output line to ‘0’; | |||
}; | |||
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
</source> | |||
===Loopback and Bypass Modes=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-Loopback-Test.png|550px|center|LMS6002D Loopback and Test Options]] | |||
===Envelop and Pick Detector Multiplexer=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-Envelop-Pick-Detector.png|550px|center|LMS6002D Envelop/Pick Detector Analogue MUX]] | |||
===TX/RX PLL=== | |||
The frequency setting for both TX and RX PLLs is the same as described here. TX PLL SPI registers are at x001xxxx and TX PLL registers are at x010xxxx. | |||
To configure the PLL there are a number of variables which need to be set. | |||
* Integer and fractional part of the divider. | |||
* FRANGE value. | |||
* VCO CAP, charge pump current (Icp) and charge pump offset current (Ioff). | |||
This assumes the given loop filter value with a loop BW of 100kHz is used. | |||
====FREQSEL==== | |||
To simplify the TX/RX PLL register setup the FRANGE and SELVCO register are combined to FREQSEL register. The frequency range and FREQSEL[5:0] value table is reproduced below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!colspan="3"|FREQSEL[5:0] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | !colspan="2"|Freuency Range (GHz) !! Value | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.2325 || 0.285625 || 100111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.285625 || 0.336875 || 101111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.336875 || 0.405 || 110111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.405 || 0.465 || 111111 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.465 || 0.57125 || 100110 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.57125 || 0.67375 || 101110 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.67375 || 0.81 || 110110 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.81 || 0.93 || 111110 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0.93 || 1.1425 || 100101 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1.1425 || 1.3475 || 101101 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1.3475 || 1.62 || 110101 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1.62 || 1.86 || 111101 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1.86 || 2.285 || 100100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2.285 || 2.695 || 101100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2.695 || 3.24 || 110100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3.24 || 3.72 || 111100 | ||
|} | |||
For example, UMTS Band I centre frequency 2140MHz is in the range 1.86 to 2.285GHz, hence FREQSEL = 100100 (0x24). | |||
====Integer and Fractional Part of the Divider==== | |||
For wanted LO frequency <math>\mathit{f_{LO}}</math> and given PLL reference clock frequency <math>\mathit{f_{REF}}</math>, calculate calculate integer and fractional part of the divider as below. | |||
First, find temporary variable <math>x</math> from the 3 least significant bits of the <math>\mathit{FREQSEL}</math> value: | |||
<math>x = 2 ^ {\mathit{FREQSEL}[2:0] - 3}</math> | |||
Use x to calculate <math>\mathit{NINT}</math> and <math>\mathit{NFRAC}</math>: | |||
<math>\mathit{NINT} = \biggl\lfloor {x * \mathit{f_{LO}} \over \mathit{f_{REF}}} \biggr\rfloor</math> | |||
<math>\mathit{NFRAC} = \biggl\lfloor 2 ^ {23} \biggl[ {x * \mathit{f_{LO}} \over \mathit{f_{REF}}} - \mathit{NINT} \biggr] \biggr\rfloor</math> | |||
and store the values in <math>\mathit{NINT}</math>/<math>\mathit{NFRAC}</math> registers at address 0x10-0x13 for TXPLL and 0x20-0x23 for RX PLL. | |||
For example <math>\mathit{f_{LO}}</math> is band 1 centre frequency of 2140MHz, and <math>\mathit{f_{REF}}</math> = 30.72MHz: | |||
<math>\mathit{FREQSEL}[5:0] = 0\mathrm{b}100100, \mathit{FREQSEL}[2:0] = 0\mathrm{b}100 = 0 \mathrm{x} 4 = 4</math> | |||
<math>x = 2 ^ {\mathit{FREQSEL}[2:0] - 3} = 2 ^ {4 - 3} = 2 ^ 1 = 2</math> | |||
<math>\mathit{NINT} = \biggl\lfloor {x * \mathit{f_{LO}} \over \mathit{f_{REF}}} \biggr\rfloor = \biggl\lfloor {2 * 2140 \over 30.72} \biggr\rfloor = 139</math> | |||
<math>\mathit{NFRAC} = \biggl\lfloor 2 ^ {23} \biggl[ {x * \mathit{f_{LO}} \over \mathit{f_{REF}}} - \mathit{NINT} \biggr] \biggr\rfloor = \biggl\lfloor 2 ^ {23} \biggl[ {2 * 2140 \over 30.72} - 139 \biggr] \biggr\rfloor = 2708821</math> | |||
====VCO Capacitor, Icp and Ioff Selection==== | |||
For the PLL loop filter implemented on the evaluation board, loop bandwidth of 100kHz and optimum PLL phase noise performance, the following charge pump current setup is recommended. | |||
* Charge pump current Icp=1200uA (default). | |||
* Charge pump current offset up Ioff up = 30uA. | |||
* Charge pump current offset down Ioff down = 0uA (default). | |||
Regarding VCOCAP selection, a flexible algorithm based on monitoring on chip Vtune comparators state is developed as described below. | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-VCO-Capacitance-Selection.png|550px|center|LMS6002 VCO Capacitance Selection]] | |||
Typical measured Vtune variation with the VCOCAP codes for the two target LO frequencies, 1.95GHz and 2.14GHz. Obviously, Vtune is changing from 2.9V down to 0V. However, PLL lock is guaranteed only when Vtune is in the range 0.5V-2.5V. Also, for the best phase noise performance, Vtune should be kept around the middle of the range i.e. 1.5V. | |||
There are two on chip Vtune comparators per PLL as shown in [[#PLL Control|PLL Control]]. Their threshold voltages are set to Vth Low=0.5V and Vth High=2.5V. The state of the comparators can be obtained by powering them up (register 0x1B for TXPLL or 0x2B for RXPLL, bit 3) and reading the register 0x1A for TXPPLL or 0x2A for RXPLL, bits 7-6. True table is given below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! VTUNE H !! VTUNE L !! Status | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || 0 || OK, Vtune in range. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || 0 || Vtune is high (> 2.5V), PLL lock not guaranteed. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 0 || 1 || Vtune is Low (< 0.5V), PLL lock not guaranteed. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || 1 || Not possible, check SPI connections. | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | These can be used to choose VCOCAP code. All we need to find is the code CMIN when comparators change the state from “10” to “00” and the code CMAX when the comparators change the state from “00” to “01”. Optimum VCOCAP code is then the middle one between CMIN and CMAX. For LO=2.4GHz, this is illustrated in [[#VCO Capacitor, Icp and Ioff Selection|VCO Capacitor, Icp and Ioff Selection]]. In this case, optimum code is around 41. | ||
[[File:LMS6002D- | |||
The algorithm is summarised as below. | |||
# Select correct [[#FREQSEL|FREQSEL]]. | |||
# Set target LO frequency (NINT, NFRAC) as explained in [[#Integer and Fractional Part of the Divider|Integer and Fractional Part of the Divider]] | |||
# Sweep VCOCAP codes from 0-63. Monitor the state of Vtune comparators. | |||
## Record the code CMIN when Vtune comparators state changes from "10" to "00" (PLL enters 'in range' state). | |||
## Record the code CMAX when Vtune comparators state changes from "00" to "01" (PLL leaves 'in range' state). | |||
## Select the middle code between CMIN and CMAX ( C=(CMIN+CMAX)/2 ). | |||
Note that faster search algorithm (replacement for step 3 above) can be implemented as shown in [[#VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm|VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm]]. | |||
Once the PLL is set, Vtune comparators can also be used as lock (in range) indication. | |||
====PLL Control==== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-PLL-Control.png|550px|center|LMS6002D PLL Control]] | |||
===TX/RF LPF=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-TXRX-LPF-Control.png|550px|center|LMS6002D TX/RX LPF Control]] | |||
===TX RF=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-TXRF-Control.png|550px|center|LMS6002D TX RF Control]] | |||
===RXVGA2=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-RXVGA2-Control.png|550px|center|LMS6002D RXVGA2 Control]] | |||
===RX FE=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-RXFE-Control.png|550px|center|LMS6002D RX FE Control]] | |||
==Calibration Flow Charts== | |||
===General DC Calibration Procedure=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-General-DC-Calibration.png|550px|center|LMS6002D General DC Calibration Flow Chart]] | |||
===DC Offset Calibration of LPF Tuning Module=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-DC-Offset-Calibration-LPF-Tuning-Module.png|550px|center|LMS6002D DC Offset Calibration of LPF Tuning Module Flow Chart]] | |||
===TX/RX LPF DC Offset Calibration=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-TXRX-LPF-DC-Offset-Calibration.png|550px|center|LMS6002D TX/RX LPF DC Offset Calibration Flow Chart]] | |||
===RXVGA2 DC Offset Calibration=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-RXVGA2-DC-Offset-Calibration.png|550px|center|LMS6002D RXVGA2 DC Offset Calibration Flow Chart]] | |||
===LPF Bandwidth Tuning=== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-LPF-Bandwidth-Tuning.png|550px|center|LMS6002D LPF Bandwidth Tuning Flow Chart]] | |||
===VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm=== | |||
====General Procedure==== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-VCO-VCOCAP-Code-Selection-Algorithm-General.png|550px|center|LMS6002D VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm, General Procedure Flow Chart]] | |||
====VCO Selection==== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-VCO-VCOCAP-Code-Selection-Algorithm-VCO-Selection.png|550px|center|LMS6002D VCO Code Selection Algorithm Flow Chart]] | |||
====VCOCAP Selection==== | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-VCO-VCOCAP-Code-Selection-Algorithm-VCOCAP-Selection.png|550px|center|LMS6002D VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm Flow Chart]] | |||
===Auto Calibration Summary=== | |||
The following is recommended auto calibration sequence. | |||
# [[#DC Offset Calibration of LPF Tuning Module|DC offset cancellation of the LPF tuning module]]. | |||
# [[#LPF Bandwidth Tuning|LPF bandwidth tuning]]. | |||
# [[#TX/RX LPF DC Offset Calibration|DC offset cancellation of the TXLPF]]. | |||
# [[#TX/RX LPF DC Offset Calibration|DC offset cancellation of the RXLPF]]. | |||
# [[#RXVGA2 DC Offset Calibration|DC offset cancellation of the RXVGA2]]. | |||
Please note, while executing DC calibration procedures no TX/RX inputs should be applied. | |||
LMS6002D has on-chip DACs for TX LO leakage calibration. Those DACs have been designed to provide around -50/-60dBc LO leakage cancellation. | |||
===Correction and Measurement Functions Implemented in BB=== | |||
====Applying IQ Gain Offset to Baseband Signals==== | |||
Software in baseband initially applies course gain variation on the I or Q channel and measures the loopbacked signal via the LMS6002D receiver to measure the optimum value. The example block for gain correction is shown below. | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-IQ-Gain-Correction.png|550px|center|LMS6002D Gain Correction Block Diagram]] | |||
This block implements the following equation: | |||
<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\mathit{Iout} = \mathit{Iin} * \mathit{G\_I} \\ | |||
\mathit{Qout} = \mathit{Qin} * \mathit{G\_Q} | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
<math>\mathit{G\_I}</math> and <math>\mathit{G\_Q}</math> are programmable correction factors which are altered by the BB modem to minimise unwanted side band component. | |||
====Applying IQ Phase Band Offset Baseband Signals==== | |||
The baseband S/W applies a course phase multiplier on the I or Q channel and measures the loopbacked signal via the LMS6002D receiver to measure the optimum value. The process is then repeated using a finer control step to ascertain the optimum phase and gain offset value to be applied. The example block for gain correction shown below. | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-IQ-Phase-Correction.png|550px|center|LMS6002D Phase Correction Block Diagram]] | |||
IQ phase correction is in fact equivalent to vector rotation. If quadrature phase error is <math>\alpha</math>, then I and Q vectors are both rotated by <math>\alpha/2</math> but in opposite directions hence IQ outputs of the corrector are 90° phase shifted. IQ phase correction equations are given below: | |||
<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\mathit{Iout} = \mathit{Iin} + \mathit{Qin} * \tan \biggl( {\alpha \over 2} \biggr) \\ | |||
\mathit{Qout} = \mathit{Qin} + \mathit{Iin} * \tan \biggl( {\alpha \over 2} \biggr) | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
The value of <math>\tan(\alpha/2)</math> is used as programmable correction parameter. BB modem should alter this value to minimize unwanted side band component. | |||
====Correcting RX I and Q DC Levels==== | |||
Software in the receiver baseband is required to calibrate the DC level on the I and Q channel received. The process of applying DC level adjustment to the I & Q channel is an optional requirement required for fine tuning purposes only. The methodology of correcting the DC levels is shown in the diagram below. | |||
[[File:LMS6002Dr2-RX-I-Q-DC-Level-Correction.png|550px|center|LMS6002D RX I and Q DC Level Correction Block Diagram]] | |||
The averaging (COMB) filter calculates the DC of the corrector input and that DC is subtracted to cancel it. The loop is running all the time so any change of the RX DC due to the signal level change, RX gain change or temperature will be tracked and cancelled automatically. The loop only programmable parameter is DCAVG which defines averaging window size. | |||
{{LimeMicro}} | {{LimeMicro}} | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 16 September 2015
Serial Port Interface
Description
The functionality of the LMS6002 transceiver is fully controlled by a set of internal registers which can be accessed through a serial port interface. Both write and read operations are supported. The serial port can be configured to run in 3 or 4 wire mode with the following pins used:
- SEN - serial port enable, active low
- SCLK - serial clock
- SDIO - serial data in/out in 3 wire mode, serial data input in 4 wire mode
- SDO-serial data out in 4 wire mode, don’t care in 3 wire mode
Serial port key features:
- 16 serial clock cycles are required to complete write operation
- 16 serial clock cycles are required to complete read operation
- Multiple write/read operations are possible without toggling serial enable signal
All configuration registers are 8-bit wide. Write/read sequence consists of 8-bit instruction followed by 8-bit data to write or read. The MSB of the instruction bit stream is used as SPI command, where CMD = 1 for write and CMD = 0 for read. Next 3 bits represent the block address, since LMS6002 configuration registers are divided into eight logical blocks as shown in the LMS6002Dr2 Memory Map. The remaining 4 bits of the instruction are used to address particular registers within the block as detailed in the Memory Map Description. Use address values from the tables.
Write/read cycle waveforms are shown below. Note that write operation is the same for both 3-wire and 4-wire modes. Although not shown in the figures, multiple byte write/read is possible by repeating instruction/data sequence while keeping SEN low.
Write Operation Waveform
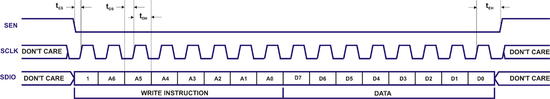
Read Operation Waveform, 4-Wire (Default)
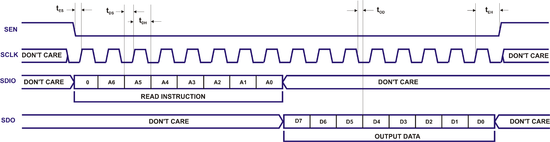
Read Operation Waveform, 3-Wire

Memory Map Description
Memory Map
| Address (7 bits) | Description |
|---|---|
| x000:xxxx | Top level configuration (as in Top Level Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x001:xxxx | TX PLL configuration (as in TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x010:xxxx | RX PLL configuration (as in TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x011:xxxx | TX LPF modules configuration (as in TX LPF Modules Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x100:xxxx | TX RF modules configuration (as in TX RF Modules Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x101:xxxx | RX LPF, DAC/ADC modules configuration (as in RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x110:xxxx | RX VGA2 configuration (as in RX VGA2 Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
| x111:xxxx | RX FE modules configuration (as in RX FE Modules Configuration (User Mode), (Test Mode)) |
Top Level Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 7-6 | Not used | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x01 | 7-5 | RCCAL_LPFCAL[2:0]: Value of the cal_core block in the LPF which calibrates the RC time constant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | DC_CLBR_DONE : indicates calibration status.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x02 | 7-6 | Not used | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011111 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x03 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-0 | DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x04 | 7-4 | VER[3:0]: Chip version. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | REV[3:0]: Chip revision. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00100010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x05 | 7 | DECODE:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Not used. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | SRESET: DSM soft reset.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | EN: Top modules enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | STXEN: Soft transmit enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | SRXEN: Soft receive enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | TFWMODE: Serial port mode.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | Not used. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00110010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x06 | 7-4 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | CLKSEL_LPFCAL: Select the clock for LPF tuning module.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | PD_CLKLPFCAL: Power down on-chip LPF tuning clock generation block.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | ENF_EN_CAL_LPFCAL: Enables the enforce mode. Passes FORCE_CODE_CAL_LPFCAL to RCCAL_LPFCAL.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | RST_CAL_LPFCAL: Reset signal used at the beginning of calibration cycle. Reset signal needs to be longer than 100ns.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001101 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x07 | 7 | EN_CAL_LPFCAL: Enable signal. If =1--> the block is enabled. Should be enabled only when the RC calibration algorithm is running.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-4 | FORCE_CODE_CAL_LPFCAL[2:0]: Input code coming from software. Will be passed to the output if ENF_EN_CAL_LPFCAL=1.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | BWC_LPFCAL[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control. (Set this code to RXLPF BWC if RXLPF and TXLPF have different cut-off frequencies).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x08 | 7 | Reserved.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | LBEN_LPFIN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to RXLPF input. If enabled, RXTIA should be disabled (powered down)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | LBEN_VGA2IN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to RXVGA2 input. If enabled, LPF should be disabled (powered down).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | LBEN_OPIN: BB loopback enable. If =1, TX BB loopback signal is connected to the RX output pins. If enabled, RXLPF and RXVGA2 should be disabled (powered down)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | LBRFEN[3:0]: RF loop back control. When activated, LNAs should be disabled (powered down).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x09 | 7 | RXOUTSW: RX out/ADC in high-Z switch control.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-0 | CLK_EN[6:0]: Clock distribution control. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | CLK_EN [6]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | CLK_EN [5]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | CLK_EN [4]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | CLK_EN [3]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | CLK_EN [2]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | CLK_EN [1]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | CLK_EN [0]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 01000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x0A | 7-2 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | FDDTDD: Frequency/Time division duplexing selection.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | TDDMOD: TDD mode selection if FDDTDD=1.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 |
Top Level Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0B | 7-5 | Not used. |
| 4 | PDXCOBUF: XCO buffer power down.
| |
| 3 | SLFBXCOBUF: XCO buffer self-biasing control.
| |
| 2 | BYPXCOBUF: XCO buffer bypass.
| |
| 1-0 | PD[1:0]: Power down control for top modules.
PD[1]
PD[0]
| |
| Default: 00001000 | ||
| 0x0E- | 5-0 | 00000001 – v1 |
| Read only. | ||
| 0x0F | 7-0 | SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. |
| Default: 00000000 |
TX/RX PLL Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tx: 0x10, Rx: 0x20 | 7-0 | NINT[8:1]: Integer part of the divider (MSBs).* |
| Default: ”01000001“0, NINT=130. | ||
| Tx: 0x11, Rx: 0x21 | 7 | NINT[0]: Integer part of the divider (LSB).* |
| 6-0 | NFRAC[22:16]: Fractional part of the divider* | |
| Tx: 0x12, Rx: 0x22 | 7-0 | NFRAC[15:8] * |
| Tx: 0x13, Rx: 0x23 | 7-0 | NFRAC[7:0] * |
| Default: 0”010…0”, NFRAC=0.25, fVCO=130.25*40MHz=5.21GHz. | ||
| Tx: 0x14, Rx: 0x24 | 7 | DITHEN: Dithering control.
|
| 6-4 | DITHN[2:0]: How many bits to dither if DITHEN=1
| |
| 3 | EN: PLL enable.
| |
| 2 | AUTOBYP: Delta sigma auto bypass when NFRAC = 0.
| |
| 1 | DECODE.
| |
| 0 | Reserved
| |
| Default: “10001000” | ||
| Tx: 0x15, Rx: 0x25 | 7-4 | SELVCO[2:0]: VCO selection.
|
| 4-2 | FRANGE[2:0]: PLL output frequency range selection.
| |
| 1-0 | SELOUT[1:0]: Select output buffer in RX PLL, not used in TX PLL.
| |
| Default: “10110001” | ||
| Tx: 0x16, Rx: 0x26 | 7 | EN_PFD_UP: Enable PFD UP pulses.
|
| 6 | OEN_TSTD_SX.
| |
| 5 | PASSEN_TSTOD_SD.
| |
| 4-0 | CHP[4:0]: Charge pump current. Binary coded, LSB = 100uA.
| |
| Default: “10001100”, ICHP = 1.2mA | ||
| Tx: 0x17, Rx: 0x27 | 7 | BYPVCOREG: Bypass VCO regulator.
|
| 6 | PDVCOREG: VCO regulator power down.
| |
| 5 | FSTVCOBG: VCO regulator band gap settling time control. Shorts the resistor in band gap to speed up charging for faster response. After the initial charge up, it should be disabled.
| |
| 4-0 | OFFUP[4:0]: Charge pump UP offset current. Binary coded, LSB = 10uA.
| |
| Default: “11100000” = 0mA. | ||
| Tx: 0x18, Rx: 0x28 | 7-5 | VOVCOREG[3:1]: VCO regulator output voltage control, 3 MSBs. LSB=100mV, VOVCOREG[3:0] coded as below.
|
| 4-0 | OFFDOWN[4:0]: Charge pump DOWN offset current. Binary coded, LSB = 10uA.
| |
| Default: “01000000” = 0mA. | ||
| Tx: 0x19, Rx: 0x29 | 7 | VOVCOREG[0]: VCO regulator output voltage control, LSB. |
| 6 | Not used. | |
| 5-0 | VCOCAP[5:0]: Switch capacitance programming. Binary coded.
| |
| Default: “10010100", VCOCAP=20 |
- Shadow registered
TX/RX PLL Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tx: 0x1A, Rx: 0x2A | 7 | VTUNE_H (Read Only): Value from Vtune comparator. |
| 6 | VTUNE_L (Read Only): Value from Vtune comparator. | |
| 5-0 | Reserved
| |
| Default: “00000011” | ||
| Tx: 0x1B, Rx: 0x2B | 7-4 | Reserved
|
| 3 | PD_VCOCOMP_SX: VCO Comparator enable.
| |
| 2 | Reserved.
| |
| 1 | Reserved.
| |
| 0 | Reserved.
| |
| Default: “01110110”, A value = 0, (N=130). | ||
| Tx: 0x1C, Rx: 0x2C | 7-0 | Reserved. |
| Default: “00111000” | ||
| Tx: 0x1D, Rx: 0x2D | 7-0 | Reserved. |
| Read only. | ||
| Tx: 0x1E, Rx: 0x2E | 7-0 | Reserved. |
| Read only. | ||
| Tx: 0x1F, Rx: 0x2F | 7-0 | Reserved. |
| Read only. |
TX LPF Modules Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x30 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x31 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | DC_CLBR_DONE: indicates calibration status.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x32 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_CNTVAL[5:0]: Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011111 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x33 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of module selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | DC_SRESET: Resets all DC Calibration modules.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-0 | DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x34 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-2 | BWC_LPF[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | EN : LPF modules enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DECODE.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x35
DCO_DACCAL_LPF renamed, no action required. |
7 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | BYP_EN_LPF: LPF bypass enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DCO_DACCAL[5:0]: Resistor calibration control for the DC offset cancellation DAC.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001100 |
TX LPF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x36 | 7 | TX_DACBUF_PD: TX data DAC buffers power down.
|
| 6-4 | RCCAL_LPF[2:0]: Calibration value, coming from TRX_LPF_CAL module.
| |
| 3 | Not used. | |
| 2 | PD_DCODAC_LPF: Power down for the DAC in the DC offset cancellation block.
| |
| 1 | PD_DCOREF_LPF: Power down signal for the dc_ref_con3 block.
| |
| 0 | PD_FIL_LPF: Power down for the filter.
| |
| Default: 00110000 | ||
| 0x3E | 7-0 | SPARE0[7:0]: Spare configuration register. |
| Default: 00000000 | ||
| 0x3F | 7 | PD_DCOCMP_LPF: Power down DC offset comparators in DC offset cancellation block. Should be powered up only when DC offset cancellation algorithm is running.
|
| 6-0 | SPARE1[6:0]: Spare configuration register | |
| Default: 00000000 |
RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x50 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC Calibration module, selected by DC_ADDR. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x51 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | DC_CLBR_DONE: indicates calibration status.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x52 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011111 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x53 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-0 | DC_ADDR[3:0]: Active calibration module address.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x54 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-2 | BWC_LPF[3:0]: LPF bandwidth control.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | EN : LPF modules enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DECODE.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x55 | 7 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | BYP_EN_LPF: LPF bypass enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DCO_DACCAL[5:0]: Resistor calibration control for the DC offset cancellation DAC.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x56 | 7 | TX_DACBUF_PD: Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-4 | RCCAL_LPF[2:0]: Calibration value, coming from TRX_LPF_CAL module.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Not used. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | PD_DCODAC_LPF: Power down for the DAC in the DC offset cancellation block.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | PD_DCOREF_LPF: Power down signal for the dc_ref_con3 block.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | PD_FIL_LPF: Power down for the filter.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00110000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x57 | 7 | EN_ADC_DAC : ADC/DAC modules enable.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | DECODE.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-3 | TX_CTRL1[6:4]. DAC Internal Output Load Resistor Control Bits.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | TX_CTRL1[3]. DAC Reference Current Resistor.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-0 | TX_CTRL1[1:0]. DAC Full Scale Output Current Control (single-ended).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 10010100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x58 | 7-6 | RX_CTRL1[7:6]. Reference bias resistor adjust.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | RX_CTRL1[5:4]. Reference bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | RX_CTRL1[3:0]. Reference bias DOWN.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x59 | 7 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-5 | RX_CTRL2[7:6]. Reference Gain Adjust.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | RX_CTRL2[5:4]. Common Mode Adjust.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-1 | RX_CTRL2[3:2]. Reference Buffer Boost.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | RX_CTRL2[0]. ADC Input Buffer Disable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x5A | 7 | MISC_CTRL[9]. Rx Fsync Polarity, frame start.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | MISC_CTRL[8]. Rx Interleave Mode.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | MISC_CTRL[7]. DAC Clk Edge Polarity.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | MISC_CTRL[6]. Tx Fsync Polarity, frame start.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | MISC_CTRL[5]. Tx Interleave Mode.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | RX_CTRL3[7]. ADC Sampling Phase Select.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-0 | RX_CTRL3[1:0]. Clock Non-Overlap Adjust.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00100000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x5B | 7-6 | RX_CTRL4[7:6] ADC bias resistor adjust.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | RX_CTRL4[5:4]. Main bias DOWN.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | RX_CTRL4[3:2]. ADC Amp1 stage1 bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-0 | RX_CTRL4[1:0]. ADC Amp2-4 stage1 bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x5C | 7-6 | RX_CTRL5[7:6] ADC Amp1 stage2 bias UP.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | RX_CTRL5[5:4]. ADC Amp2-4 stage2 bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | RX_CTRL5[3:2]. Quantizer bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-0 | RX_CTRL5[1:0]. Input Buffer bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x5D | 7-4 | REF_CTRL0[7:4]. Bandgap Temperature Coefficient Control.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | REF_CTRL0[3:0]. Bandgap Gain Control.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x5E | 7-6 | REF_CTRL1[7:6]. Reference Amps bias adjust.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | REF_CTRL1[5:4]. Reference Amps bias UP.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | REF_CTRL1[3:0]. Reference Amps bias DOWN.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 |
RX LPF, DAC/ADC Modules Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0X5F | 7 | PD_DCOCMP_LPF: Power down DC offset comparators in DC offset cancellation block. Should be powered up only when DC offset cancellation algorithm is running.
|
| 6-5 | SPARE00[6:5]: Spare configuration bits.
| |
| 4 | MISC_CTRL[4]. Enable DAC.
| |
| 3 | MISC_CTRL[3]. Enable ADC1 (I Channel).
| |
| 2 | MISC_CTRL[2]. Enable ADC2 (Q Channel).
| |
| 1 | MISC_CTRL[1]. Enable ADC reference.
| |
| 0 | MISC_CTRL[0]. Enable master reference.
| |
| Default: 00011111 |
TX RF Modules Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x40 | 7-2 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | EN : TXRF modules enable
| ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DECODE:
| ||||||||||||||||
| 0x41 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||
| 4-0 | VGA1GAIN[4:0]: TXVGA1 gain, log-linear control. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00010101 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x42 | 7-0 | VGA1DC_I[7:0]: TXVGA1 DC shift control, LO leakage cancellation. LSB=0.0625mV, encoded as shown below.
| |||||||||||||||
| Default: 10000000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x43 | 7-0 | VGA1DC_Q[7:0]: TXVGA1 DC shift control, LO leakage cancellation LSB=0.0625mV, encoded as shown below.
| |||||||||||||||
| Default: 10000000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x44 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | PA_EN[2:0]: VGA2 power amplifier (TX output) selection.
| ||||||||||||||||
| 2 | PA_EN[2]: AUXPA, auxiliary (RF loopack) PA power down.
| ||||||||||||||||
| 1-0 | Not used. | ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001011 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x45 | 7-3 | VGA2GAIN[4:0]: TXVGA2 gain control, log-linear control. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below.
| |||||||||||||||
| 2-0 | ENVD[2:0]: Controls envelop/peak detector analogue MUX.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x46 | 7-4 | PKDBW[3:0]: Controls the bandwidth of the envelop and peak detectors.
| |||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | LOOPBBEN[1:0]: Base band loopback switches control.
| ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | FST_PKDET: Shorts the resistor in the envelop/peak detector to speed up charging for faster response. After the initial charge up, it should be disabled to achieve a LPF function.
| ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | FST_TXHFBIAS: Bias stage of high frequency TX part has large resistors to filter the noise. However, they create large settling time. This switch can be used to short those resistors during the initialization and then it may be needed to open it to filter the noise, in case the noise is too high.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x47 | 7-4 | ICT_TXLOBUF[3:0]: Controls the bias current of the LO buffer. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=5/6mA.
| |||||||||||||||
| 3-0 | VBCAS_TXDRV[3:0]: The linearity of PAs depends on the bias at the base of the cascode NPNs in the PA cells. Increasing the VBCAS will lower the base of the cascode NPN.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 01100000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x48 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||
| 4-0 | ICT_TXMIX[4:0]: Controls the bias current of the mixer. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=1mA.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001100 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0x49 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||
| 4-0 | ICT_TXDRV[4:0]: Controls the bias current of the PAs. Higher current will increase the linearity. LSB=1mA.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001100 |
TX RF Modules Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x4A | 7-5 | Not used. | ||||||||||||||||
| 4 | PW_VGA1_I: VGA1, I channel power control.
| |||||||||||||||||
| 3 | PW_VGA1_Q: VGA1, Q channel power control.
| |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | PD_TXDRV: Power down for PAs and AUXPA.
| |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | PD_TXLOBUF: Power down for TXLOBUF.
| |||||||||||||||||
| 0 | PD_TXMIX: Power down for TXMIX.
| |||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0x4B | 7-0 | VGA1GAINT[7:0]: TXVGA1 gain control, raw access. LSB=1dB, encoded as shown below.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 01010000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0x4C | 7-0 | G_TXVGA2[8:1]: Controls the gain of PA1, PA2 and AUXPA, raw access.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000, 0dB gain. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0x4D | 7 | PD_PKDET: Power down for envelop/peak detectors.
| ||||||||||||||||
| 6-0 | SPARE0[6:0]: Spare configuration register. | |||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0x4F | 7-0 | SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 |
RX VGA2 Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x60 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_REGVAL[5:0]: Value from DC Calibration module selected by DC_ADDR. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read Only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x61 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | DC_LOCK[2:0]: Lock pattern register.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | DC_CLBR_DONE : indicates calibration status.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DC_UD: Value from DC module comparator, selected by DC_ADDR
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read only. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x62 | 7-6 | Not used | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-0 | DC_CNTVAL[5:0] : Value to load into selected (by DC_ADDR) DC calibration module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011111 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x63 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | DC_START_CLBR: Start calibration command of the module, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | DC_LOAD: Load value from DC_CNTVAL to module, selected by DC_ADDR.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | DC_SRESET: resets all DC Calibration modules.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-0 | DC_ADDR[2:0]: Active calibration module address.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00001000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x64 | 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-2 | VCM[3:0]: RXVGA2 output common mode voltage control. VCM[3] – sign, VCM[2:0] – magnitude, LSB=40mV.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | EN :RXVGA2 modules enable.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | DECODE:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00011110 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0x65 | 7-5 | Not used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-0 | VGA2GAIN[4:0]: RXVGA2 gain control. LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below.
Not recommended to be used above 30dB. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Default: 00000001 |
RX VGA2 Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x66 | PD[9:0]: Power down different modules. | |||||||||||||
| 7-6 | Not used. | |||||||||||||
| 5 | PD[9] - DC current regulator.
| |||||||||||||
| 4 | PD[8] - DC calibration DAC for VGA2B.
| |||||||||||||
| 3 | Not used. | |||||||||||||
| 2 | PD[6] - DC calibration DAC for VGA2A.
| |||||||||||||
| 1 | Not used. | |||||||||||||
| 0 | PD[4] - Band gap.
| |||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | ||||||||||||||
| 0x67 | 7-4 | Not used. | ||||||||||||
| 3 | PD[3] – Output buffer in both RXVGAs.
| |||||||||||||
| 2 | PD[2] - RXVGA2B.
| |||||||||||||
| 1 | PD[1] - RXVGA2A.
| |||||||||||||
| 0 | PD[0] - Current reference.
| |||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | ||||||||||||||
| 0x68 | 7-4 | VGA2GAINB: Controls the gain of second VGA2 stage (VGA2B). LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below.
| ||||||||||||
| 3-0 | VGA2GAINA: Controls the gain of first VGA2 stage (VGA2A). LSB=3dB, encoded as shown below.
| |||||||||||||
| Default: 00000001 | ||||||||||||||
| 0x6E | 7 | PD[7] - DC calibration comparator for VGA2B.
| ||||||||||||
| 6 | PD[6] - DC calibration comparator for VGA2A.
| |||||||||||||
| 5-0 | SPARE0[5:0]: Spare configuration register. | |||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 | ||||||||||||||
| 0x6F | 7-0 | SPARE1[7:0]: Spare configuration register. | ||||||||||||
| Default: 00000000 |
RX FE Modules Configuration (User Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x70 | 7-2 | Not used. |
| 1 | DECODE.
| |
| 0 | EN: RXFE modules enable.
| |
| Default: 00000001 | ||
| 0x71 | 7 | IN1SEL_MIX_RXFE: Selects the input to the mixer.
|
| 6-0 | DCOFF_I_RXFE[6:0]: DC offset cancellation, I channel.
| |
| Default: 10000000 | ||
| 0x72 | 7 | INLOAD_LNA_RXFE: To select the internal load for the LNA.
|
| 6-0 | DCOFF_Q_RXFE[6:0]: DC offset cancellation, Q channel.
| |
| Default: 10000000 | ||
| 0x73 | 7 | XLOAD_LNA_RXFE: To select the externa load for the LNA.
|
| 6-0 | IP2TRIM_I_RXFE[6:0]: IP2 cancellation, I channel.
| |
| Default: 00000000 | ||
| 0x75 | 7-6 | G_LNA_RXFE[1:0]: LNA gain mode control.
|
| 5-4 | LNASEL_RXFE[1:0]: Selects the active LNA.
| |
| 3-0 | CBE_LNA_RXFE[3:0]: Controls the capacitance parallel to the BE of the input NPN transistors. To be used at lower frequencies for easier matching. For LNA1 and LNA2 only.
| |
| Default: 11010000 | ||
| 0x76 | 7 | Not used. |
| 6-0 | RFB_TIA_RXFE[6:0]: Feedback resistor control of the TIA (RXVGA1) to set the mixer gain.
| |
| Default: 01111000 | ||
| 0x77 | 7 | Not used. |
| 6-0 | CFB_TIA_RXFE[6:0]: Feedback capacitor for the TIA (RXVGA1) to limit the BW.
This cap is supposed to be set according to the RC time constant to have almost constant BW over the corners for optimum CDMA performance. Software will control it using the information from the LPF calibration circuit. | |
| Default: 00000000 | ||
| 0x78 | 7-6 | Not used. |
| 5-0 | RDLEXT_LNA_RXFE[5:0]: Controls the on-chip LNA load resistor for the external load mode of the LNA. In practice, this will be set to high value, the output will be ac coupled, and the actual load is defined on PCB.
| |
| Default: 00011100 | ||
| 0x79 | 7-6 | Not used. |
| 5-0 | RDLINT_LNA_RXFE[5:0]: Controls the on-chip LNA load resistor for the internal load mode of the LNA, LNA1 and LNA2.
| |
| Default: 00011100 | ||
| 0x7A | 7-4 | ICT_MIX_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for mixer.
|
| 3-0 | ICT_LNA_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for LNA.
| |
| Default: 01110111 | ||
| 0x7B | 7-4 | ICT_TIA_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for TIA (RXVGA1).
|
| 3-0 | ICT_MXLOB_RXFE[3:0]: Control for tweaking the bias current for mixer LO buffer.
| |
| Default: 01110111 | ||
| 0x7C | 7 | Not used. |
| 6-3 | LOBN_MIX_RXFE[3:0]: Tweak for the LO bias of the mixer for optimum linearity.
| |
| 2 | RINEN_MIX_RXFE: Termination resistor on external mixer input enable.
| |
| 1-0 | G_FINE_LNA3_RXFE[1:0]: LNA3 fine gain adjustment.
| |
| Default: 00011000 |
RX FE Modules Configuration (Test Mode)
| Address (7 bits) | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x7D | 7-4 | Not used. |
| 3 | PD_TIA_RXFE: TIA (RXVGA1) power down.
| |
| 2 | PD_MXLOB_RXFE: Mixer LO buffer power down.
| |
| 1 | PD_MIX_RXFE: Mixer power down.
| |
| 0 | PD_LNA_RXFE: LNA power down.
| |
| Default: 00000000 | ||
| 0x7E | 7-0 | SPARE0[7:0] |
| Default: 00000000 | ||
| 0x7F | 7-0 | SPARE1[7:0] |
| Default: 00000000 |
Control Block Diagrams
SPI Read/Write Pseudocode
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Write command, SPI module address, register address
// Read data
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SPI_Read(BYTE COMMAND)
{
BYTE DATA; //We will read data there
//Write Command and Address (MSB First)
//First 1 bit (MSB) = Command
//Next 3 bits = SPI memory block address
//Next 4 (LSBs) bits = Register Address
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--)
{
if(i’th bit in COMMAND is ‘1’)
{
Set Data Output line to ‘1’;
}
else
{
Set Data Output line to ‘0’;
};
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line;
};
//Read Data (MSB First)
//Note: At this point we have data MSB valid from the chip.
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--)
{
if(there is ‘1’ at the Data Input Line)
{
Set i’th bit in DATA ‘1’;
}
else
{
Set i’th bit in DATA ‘0’;
};
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line;
};
};
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Write data to the chip:
// First byte: Command, SPI module address, register address
// Second byte: Data
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SPI_Write(BYTE COMMAND, BYTE DATA)
{
//Write Command, Address
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--)
{
if(i’th bit in COMMAND is ‘1’)
{
Set Data Output line to ‘1’;
}
else
{
Set Data Output line to ‘0’;
};
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line;
};
//Write Data
for(int i=7; i>=0; i--)
{
if(i’th bit in DATA is ‘1’)
{
Set Data Output line to ‘1’;
}
else
{
Set Data Output line to ‘0’;
};
Apply Rising and Falling CLK signal edges to CLK line;
};
};
Loopback and Bypass Modes
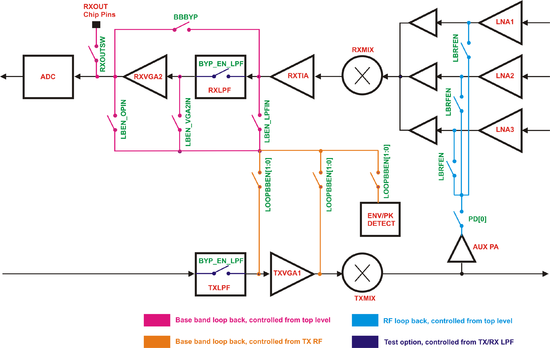
Envelop and Pick Detector Multiplexer
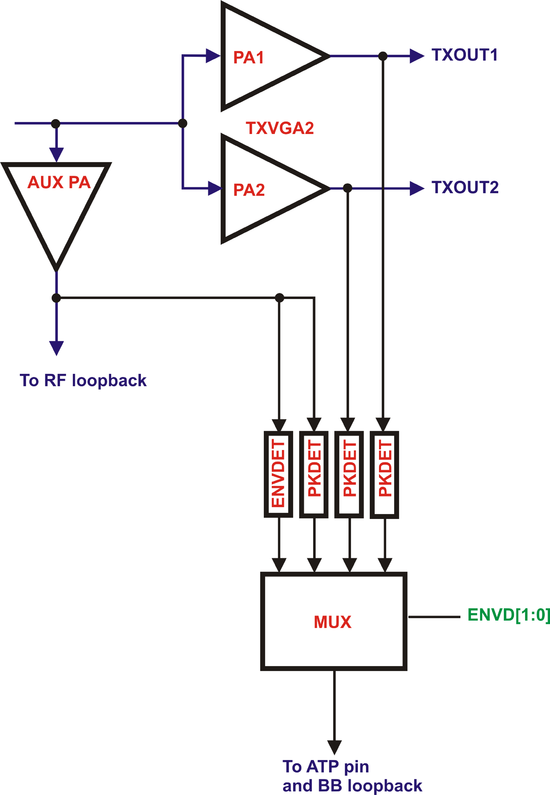
TX/RX PLL
The frequency setting for both TX and RX PLLs is the same as described here. TX PLL SPI registers are at x001xxxx and TX PLL registers are at x010xxxx.
To configure the PLL there are a number of variables which need to be set.
- Integer and fractional part of the divider.
- FRANGE value.
- VCO CAP, charge pump current (Icp) and charge pump offset current (Ioff).
This assumes the given loop filter value with a loop BW of 100kHz is used.
FREQSEL
To simplify the TX/RX PLL register setup the FRANGE and SELVCO register are combined to FREQSEL register. The frequency range and FREQSEL[5:0] value table is reproduced below.
| FREQSEL[5:0] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Freuency Range (GHz) | Value | |
| 0.2325 | 0.285625 | 100111 |
| 0.285625 | 0.336875 | 101111 |
| 0.336875 | 0.405 | 110111 |
| 0.405 | 0.465 | 111111 |
| 0.465 | 0.57125 | 100110 |
| 0.57125 | 0.67375 | 101110 |
| 0.67375 | 0.81 | 110110 |
| 0.81 | 0.93 | 111110 |
| 0.93 | 1.1425 | 100101 |
| 1.1425 | 1.3475 | 101101 |
| 1.3475 | 1.62 | 110101 |
| 1.62 | 1.86 | 111101 |
| 1.86 | 2.285 | 100100 |
| 2.285 | 2.695 | 101100 |
| 2.695 | 3.24 | 110100 |
| 3.24 | 3.72 | 111100 |
For example, UMTS Band I centre frequency 2140MHz is in the range 1.86 to 2.285GHz, hence FREQSEL = 100100 (0x24).
Integer and Fractional Part of the Divider
For wanted LO frequency and given PLL reference clock frequency , calculate calculate integer and fractional part of the divider as below.
First, find temporary variable from the 3 least significant bits of the value:
Use x to calculate and :
and store the values in / registers at address 0x10-0x13 for TXPLL and 0x20-0x23 for RX PLL.
For example is band 1 centre frequency of 2140MHz, and = 30.72MHz:
VCO Capacitor, Icp and Ioff Selection
For the PLL loop filter implemented on the evaluation board, loop bandwidth of 100kHz and optimum PLL phase noise performance, the following charge pump current setup is recommended.
- Charge pump current Icp=1200uA (default).
- Charge pump current offset up Ioff up = 30uA.
- Charge pump current offset down Ioff down = 0uA (default).
Regarding VCOCAP selection, a flexible algorithm based on monitoring on chip Vtune comparators state is developed as described below.
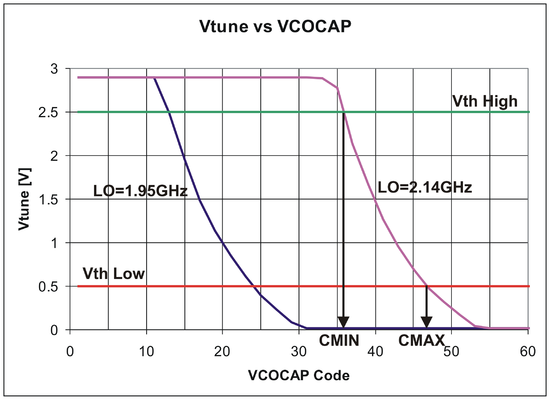
Typical measured Vtune variation with the VCOCAP codes for the two target LO frequencies, 1.95GHz and 2.14GHz. Obviously, Vtune is changing from 2.9V down to 0V. However, PLL lock is guaranteed only when Vtune is in the range 0.5V-2.5V. Also, for the best phase noise performance, Vtune should be kept around the middle of the range i.e. 1.5V.
There are two on chip Vtune comparators per PLL as shown in PLL Control. Their threshold voltages are set to Vth Low=0.5V and Vth High=2.5V. The state of the comparators can be obtained by powering them up (register 0x1B for TXPLL or 0x2B for RXPLL, bit 3) and reading the register 0x1A for TXPPLL or 0x2A for RXPLL, bits 7-6. True table is given below.
| VTUNE H | VTUNE L | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | OK, Vtune in range. |
| 1 | 0 | Vtune is high (> 2.5V), PLL lock not guaranteed. |
| 0 | 1 | Vtune is Low (< 0.5V), PLL lock not guaranteed. |
| 1 | 1 | Not possible, check SPI connections. |
These can be used to choose VCOCAP code. All we need to find is the code CMIN when comparators change the state from “10” to “00” and the code CMAX when the comparators change the state from “00” to “01”. Optimum VCOCAP code is then the middle one between CMIN and CMAX. For LO=2.4GHz, this is illustrated in VCO Capacitor, Icp and Ioff Selection. In this case, optimum code is around 41.
The algorithm is summarised as below.
- Select correct FREQSEL.
- Set target LO frequency (NINT, NFRAC) as explained in Integer and Fractional Part of the Divider
- Sweep VCOCAP codes from 0-63. Monitor the state of Vtune comparators.
- Record the code CMIN when Vtune comparators state changes from "10" to "00" (PLL enters 'in range' state).
- Record the code CMAX when Vtune comparators state changes from "00" to "01" (PLL leaves 'in range' state).
- Select the middle code between CMIN and CMAX ( C=(CMIN+CMAX)/2 ).
Note that faster search algorithm (replacement for step 3 above) can be implemented as shown in VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm.
Once the PLL is set, Vtune comparators can also be used as lock (in range) indication.
PLL Control
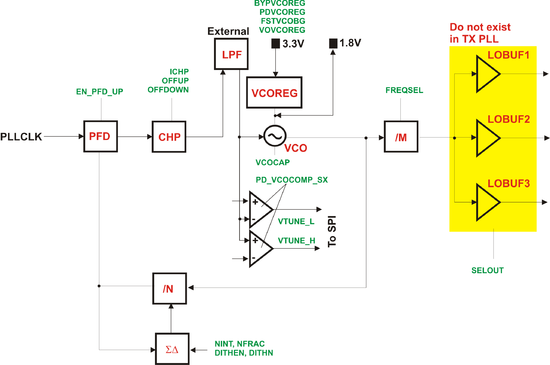
TX/RF LPF
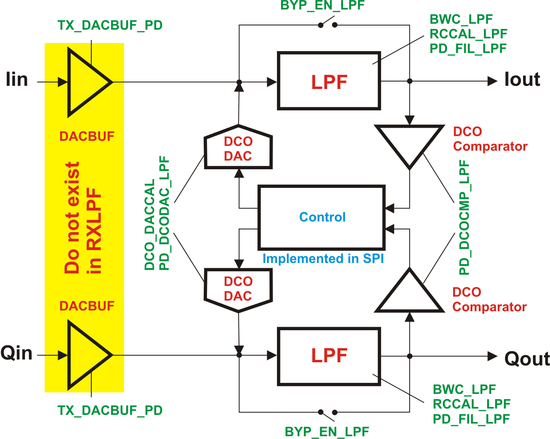
TX RF
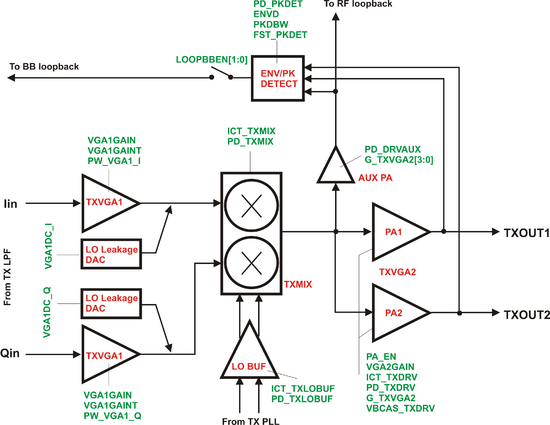
RXVGA2
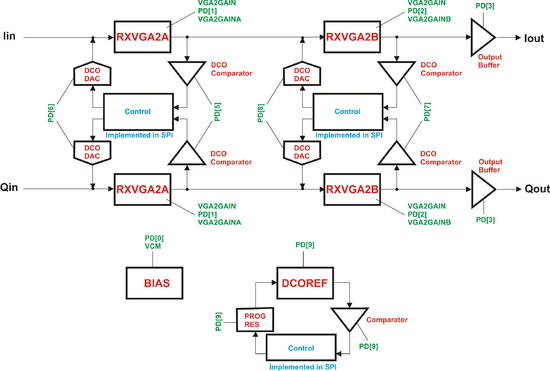
RX FE
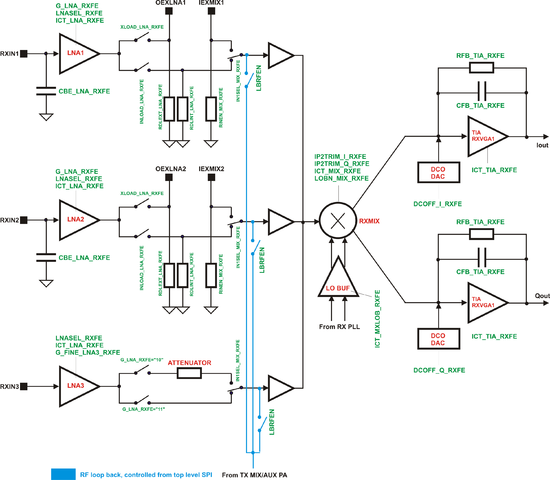
Calibration Flow Charts
General DC Calibration Procedure
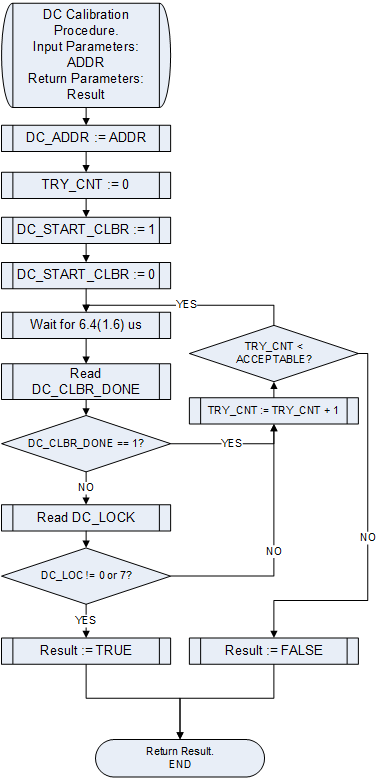
DC Offset Calibration of LPF Tuning Module
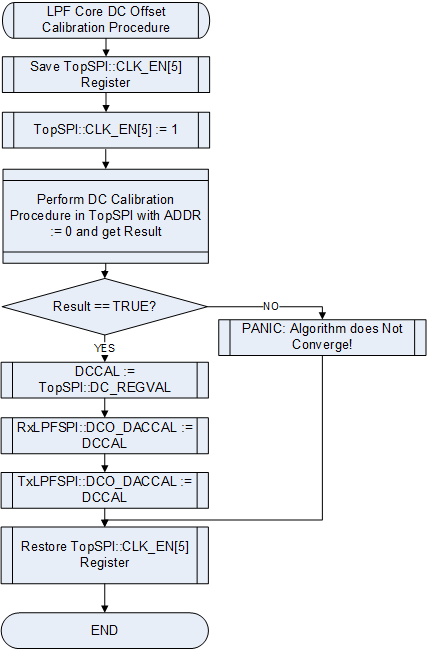
TX/RX LPF DC Offset Calibration
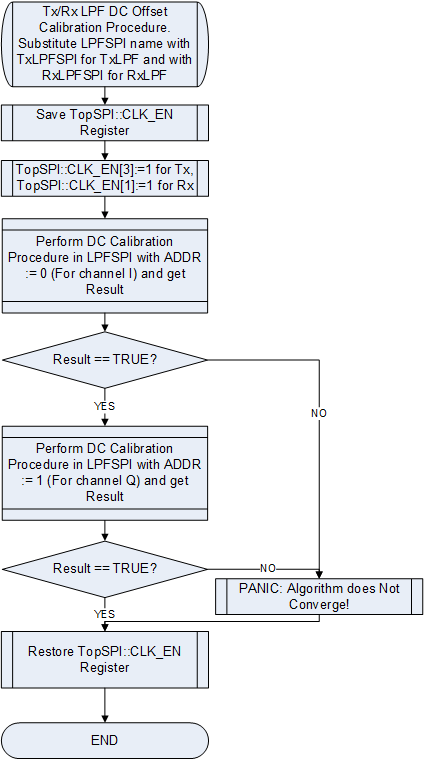
RXVGA2 DC Offset Calibration
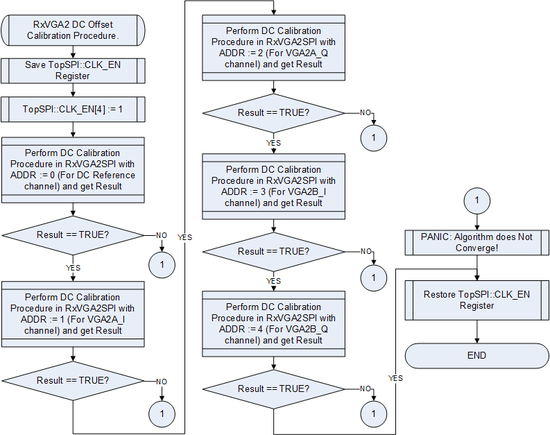
LPF Bandwidth Tuning
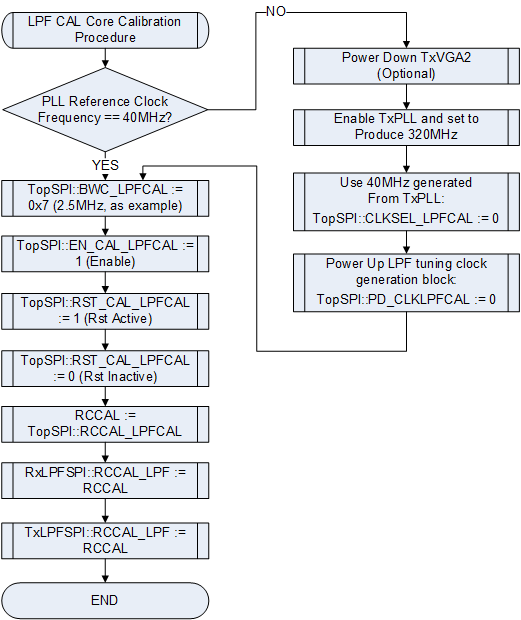
VCO and VCOCAP Code Selection Algorithm
General Procedure
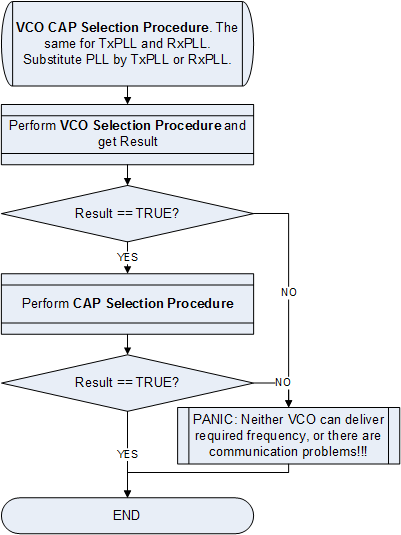
VCO Selection
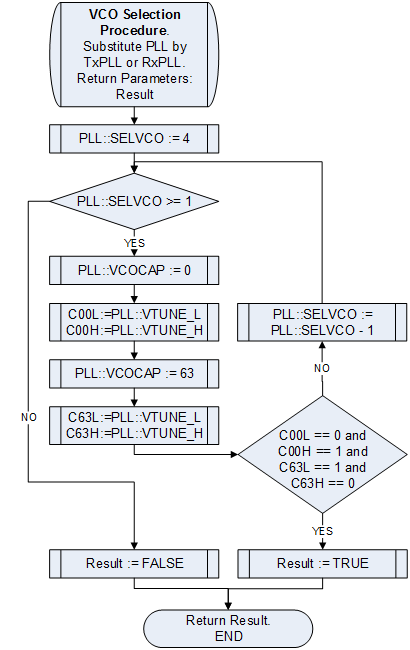
VCOCAP Selection
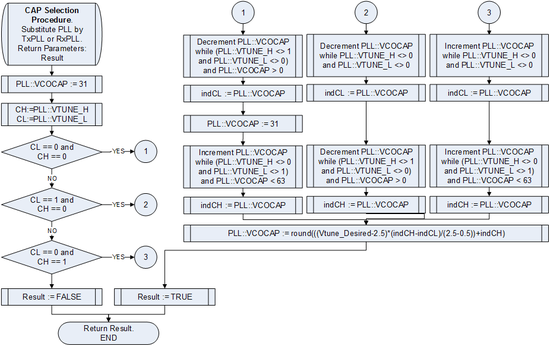
Auto Calibration Summary
The following is recommended auto calibration sequence.
- DC offset cancellation of the LPF tuning module.
- LPF bandwidth tuning.
- DC offset cancellation of the TXLPF.
- DC offset cancellation of the RXLPF.
- DC offset cancellation of the RXVGA2.
Please note, while executing DC calibration procedures no TX/RX inputs should be applied.
LMS6002D has on-chip DACs for TX LO leakage calibration. Those DACs have been designed to provide around -50/-60dBc LO leakage cancellation.
Correction and Measurement Functions Implemented in BB
Applying IQ Gain Offset to Baseband Signals
Software in baseband initially applies course gain variation on the I or Q channel and measures the loopbacked signal via the LMS6002D receiver to measure the optimum value. The example block for gain correction is shown below.
This block implements the following equation:
and are programmable correction factors which are altered by the BB modem to minimise unwanted side band component.
Applying IQ Phase Band Offset Baseband Signals
The baseband S/W applies a course phase multiplier on the I or Q channel and measures the loopbacked signal via the LMS6002D receiver to measure the optimum value. The process is then repeated using a finer control step to ascertain the optimum phase and gain offset value to be applied. The example block for gain correction shown below.
IQ phase correction is in fact equivalent to vector rotation. If quadrature phase error is , then I and Q vectors are both rotated by but in opposite directions hence IQ outputs of the corrector are 90° phase shifted. IQ phase correction equations are given below:
The value of is used as programmable correction parameter. BB modem should alter this value to minimize unwanted side band component.
Correcting RX I and Q DC Levels
Software in the receiver baseband is required to calibrate the DC level on the I and Q channel received. The process of applying DC level adjustment to the I & Q channel is an optional requirement required for fine tuning purposes only. The methodology of correcting the DC levels is shown in the diagram below.
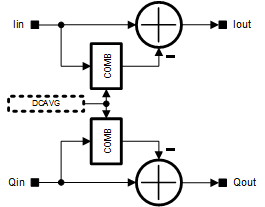
The averaging (COMB) filter calculates the DC of the corrector input and that DC is subtracted to cancel it. The loop is running all the time so any change of the RX DC due to the signal level change, RX gain change or temperature will be tracked and cancelled automatically. The loop only programmable parameter is DCAVG which defines averaging window size.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {Gain} =20*\log 10\left(0.038*{\mathit {G\_TXVGA2[8:0]}}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bf5db1b6427e81b415623cc485f0f8e5b73c479b)




![{\displaystyle x=2^{{\mathit {FREQSEL}}[2:0]-3}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/221036a02878e2ccebb16331af6a1b63cbe22f3d)



![{\displaystyle {\mathit {NFRAC}}={\biggl \lfloor }2^{23}{\biggl [}{x*{\mathit {f_{LO}}} \over {\mathit {f_{REF}}}}-{\mathit {NINT}}{\biggr ]}{\biggr \rfloor }}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/707334708e4ada774105f6408982e377e2b44acb)
![{\displaystyle {\mathit {FREQSEL}}[5:0]=0\mathrm {b} 100100,{\mathit {FREQSEL}}[2:0]=0\mathrm {b} 100=0\mathrm {x} 4=4}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b647de54bea60d3732e6605b3c8b821edc80f01a)
![{\displaystyle x=2^{{\mathit {FREQSEL}}[2:0]-3}=2^{4-3}=2^{1}=2}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be37f2336943e50d8009a68ab67f6b2c2c8b6097)

![{\displaystyle {\mathit {NFRAC}}={\biggl \lfloor }2^{23}{\biggl [}{x*{\mathit {f_{LO}}} \over {\mathit {f_{REF}}}}-{\mathit {NINT}}{\biggr ]}{\biggr \rfloor }={\biggl \lfloor }2^{23}{\biggl [}{2*2140 \over 30.72}-139{\biggr ]}{\biggr \rfloor }=2708821}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8e46523af6945c0a7a433459dc5ac82925e041d4)







