Getting Started with the LimeNET-Micro
Getting Started with LimeNET-Micro
Basic setup
Powering the board
LimeNET-Micro board can be powered in three ways:
- Power over Ethernet – using RJ45 connector and power sourcing equipment (PSE) such as PoE capable network switch or PoE injector. LimeNET-Micro board works with PSE supplying power in “Mode A/Endspan” as well in “Mode B/Midspan” modes;
- DC connector - 5V power source connected to J28 power jack should be capable to provide 2A-3A current;
- microUSB port - 5V power source connected to J15 connector should be capable to provide 2A-3A current;
Power source can be selected fitting jumper in one of the three positions on J27 header (see Figure 1):
- A (pins 5-6) – 5V micro USB;
- B (pins 3-4) – 5V external DC;
- C (pins 1-2) – Power over Ethernet;
To get LimeNET-Micro board up and running:
- Set “Power selection” jumper J27 to “A” position (pins 5-6, 5V micro USB power selection);
- Connect mouse and keyboard to J10 USB connectors;
- Connect monitor cable to J19 HDMI connector;
- Insert CM3 module into J13 socket (or CM3(L) module into J13 and uSD card into J16 slot).
- Connect power adapter (5V, 2A-3A) to micro USB connector J15.
FPGA programming
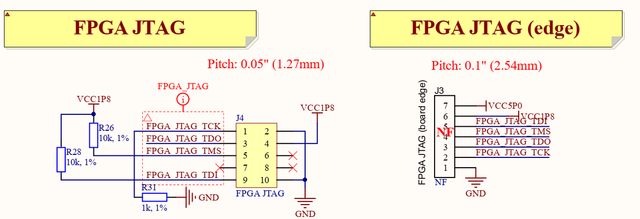
Intel MAX10 FPGA can be programmed using JTAG adapter such as Intel FPGA USB Download Cable (formerly known as Altera USB-Blaster download cable). LimeNET-Micro board has two different size and pin count JTAG headers (J4 - 10pin 0.05” pitch header and J3 - 7pin 0.1” pitch edge connector). Additional cable adapter is needed to connect download cable to LimeNET-Micro board because Intel FPGA USB Download Cable comes with 10-pin, 0.1” pitch female connector.