Lime-GPSDO v1.0 hardware description: Difference between revisions
| Line 219: | Line 219: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Table | |+ Table 5. Default LEDs functions | ||
! Board Reference !! Schematic signal name !! Board label !! FPGA pin !! Description | ! Board Reference !! Schematic signal name !! Board label !! FPGA pin !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 11 April 2019
Lime-GPSDO Board Key Features
The Lime-GPSDO development board provides high stability clock source for timing sensitive applications. Clock frequency is being constantly monitored inside MAX10 FPGA and tuned by PPS signal from GNSS module.
For more information on the following topics, refer to the respective documents:
Lime-GPSDO board features:
- USB Interface
- Silicon labs USBXpress Family USB-to-UART bridge CP2102N.
- FPGA Features
- MAX10 10M16SAU169C8 device in 169-pin UBGA
- 16K logic elements
- 549 Kbits embedded memory (M9K) and 2368 Kbits of user Flash Memory
- 45 embedded 18x18 multipliers
- 1 PLLs
- FPGA Configuration
- JTAG mode configuration
- Memory Devices
- 4Mbit FLASH
- 128Kbit (16K x 8) EEPROM
- Connections
- microUSB2.0 (type B)
- SMA connectors for clock IN/OUT, time pulse output and GNSS antenna
- FPGA GPIO header (0.05” pitch)
- FPGA JTAG connectors (0.05” pitch and side connector)
- 5V DC power jack and pinheader
- Backup battery connector for GNSS receiver
- Clock output pinheader
- External UART connector
- External I2C connector
- Clock System
- 30.72MHz VCOCXO:
- Frequency calibration ±0.5ppm;
- Frequency stability over temperature in still air ±20ppb;
- Frequency slope ΔF/ΔT in still air ±1.2ppb/°C
- Possibility to tune VCOCXO by onboard DAC
- Possibility to use GNSS PPS signal as a reference when tuning VCOCXO frequency
- 30.72MHz VCOCXO:
- Board Size without connectors 50.50mm x 80mm (1.99” x 3.15”)
Board Overview
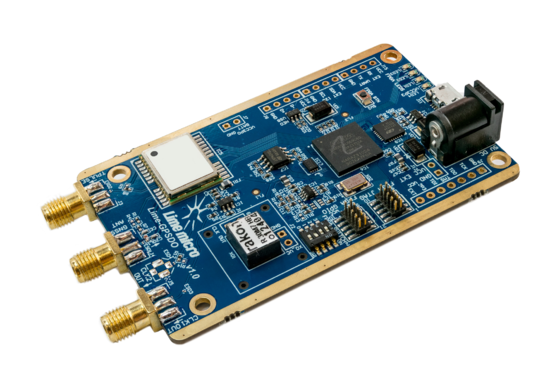
Lime-GPSDO board version 1.0 picture with highlighted major components and connections presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. There are three connector types – data and debugging (USB2.0, FPGA GPIO and JTAG), power (DC jack and external supply pinheader), clock source output, GNSS antenna and time pulse output.
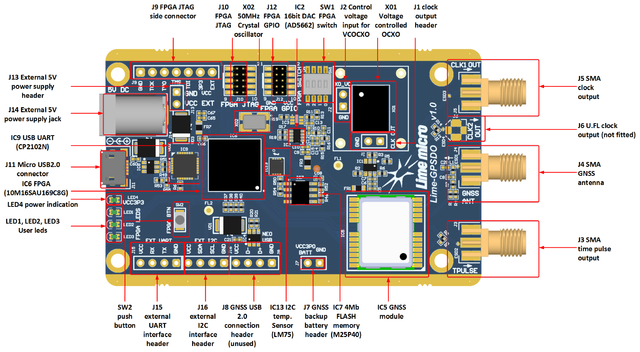
Board components description listed in the Table 1 and Table 2.
| Featured Devices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Board reference | Type | Description |
| IC5 | GNSS module | GNSS receiver |
| IC5 | FPGA | Intel MAX 10 (10M16SAU169C8G 169-UBGA) |
| IC9 | USB UART | Silicon labs USB-to-UART bridge |
| Miscellaneous devices onboard | ||
| IC13 | IC | Temperature sensor LM75 |
| Configuration, Status and Setup Components | ||
| J9 | JTAG chain pin header | FPGA programming pin header for Altera USB-Blaster download cable, side connection. |
| J10 | JTAG chain pin header | FPGA programming pin header for Altera USB-Blaster download cable, 0.05” pitch |
| LEDS1, LEDS2, LEDS3 | Red-green status LEDs | User defined FPGA indication. |
| General User Input/Output | ||
| J12 | Pin header | 8 FPGA GPIOs plus 2 power pins, 0.05” pitch |
| SW1 | Slide switch | 4 slide switches connected to FPGA |
| SW2 | Push button | Push button connected to FPGA |
| Memory Devices | ||
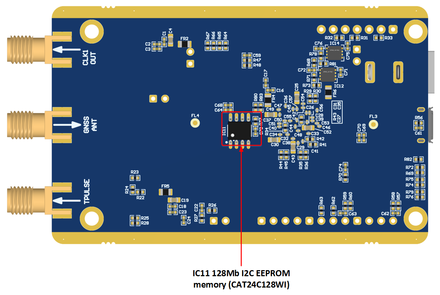
| IC11 | EEPROM | 128K (16K x 8) EEPROM connected to FPGA |
| IC10 | IC | I²C EEPROM Memory 128Kb (16K x 8), connected to FPGA I2C bus |
| IC7 | Flash memory | 4Mbit FLASH memory connected to FPGA |
| Communication Ports | ||
| J11 | USB2.0 connector | microUSB2.0 (type B) connector |
| J8 | Header | GNSS USB 2.0 connection header (unused) |
| J15 | Header | External UART interface header, can be used to control external periphery. Additional logic has to be implemented in FPGA. |
| J16 | Header | External I2C interface header, can be used to control external periphery. Additional logic has to be implemented in FPGA. |
| Clock Circuitry | ||
| XO1 | VCOCXO | 30.72MHz voltage-controlled crystal oscillator used as a reference clock. |
| XO2 | XO | 50MHz crystal oscillator, used for FPGA logic. |
| IC2 | DAC | Analog devices 16bit Digital-to-analog converter for VCOCXO voltage control |
| J1 | Pin header | Optional clock output of XO1 |
| J2 | Pin header | Optional Voltage control input for XO1 |
| J3 | SMA connector | Time pulse output from GNSS modules |
| J5 | SMA connector | Reference clock output |
| J6 | U.FL connector | Reference clock output, connector is not fitted by default. |
| Power Supply | ||
| J14 | DC input jack | External 5V DC power supply |
| J13 | Pin header | External 5V DC power supply and main internal power rail |
| Other | ||
| J4 | SMA connector | Antenna input for GNSS module |
| J7 | Pin header | Backup battery connection header for GNSS module. Typical 3.0V (follow recommendation in fitted GNSS module datasheet) |
LimeSDR-Mini Board Architecture
The heart of the Lime-GPSDO board is Intel MAX10 FPGA. Its main function is to measure VCOCXO clock frequency and tune it by PPS signal from GNSS module and provide control. The block diagram for Lime-GPSDO board is presented in the Figure 3.
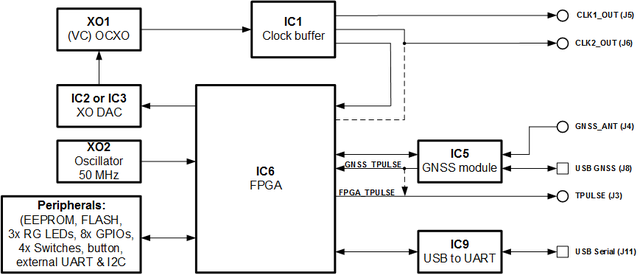
GNSS module
GNSS module has serial data communication interface, timing pulse and other control signals connected to FPGA. It also has SMA connector for external antenna.
| Chip pin (IC5) | Chip reference (IC5) | Schematic signal name | FPGA pin | FPGA I/O standard | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | TIMEPULSE | GNSS_TPULSE | A2 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | Also connected to J3 SMA conn. |
| 4 | EXTINT | GNSS_EXTINT | B1 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 8 | RESET_N | GNSS_RESET | C1 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 14 | LNA_EN /RESV | GNSS_OFF | F1 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 15 | RTK_STAT /RESV | GNSS_ANT_DET | E1 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 16 | GEOFENCE_STAT /RESV | GNSS_ANT_OK | D1 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 18 | DDC_SDA /SPI_CSN | GNSS_DDC_SDA | B2 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 19 | DDC_SCL /SPI_CLK | GNSS_DDC_SCL | A3 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 20 | UART_TX /SPI_MISO | GNSS_UART_TX | B3 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 21 | UART_RX /SPI_MOSI | GNSS_UART_RX | A4 | 3.3-V LVCMOS | |
| 11 | RF_IN | RF_IN | - | - | Connected to J4 SMA conn. |
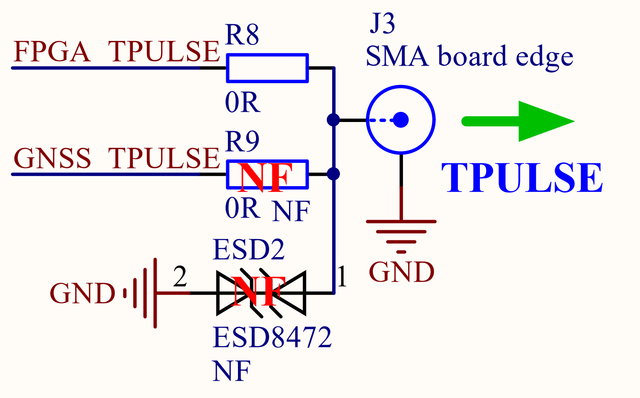
By default time pulse output (J3 SMA connector) is connected to FPGA pin C2 output but can be changed to GNSS time pulse signal by removing R8 resistor and soldering R9 resistors. Refer to Figure 4.
GPIO
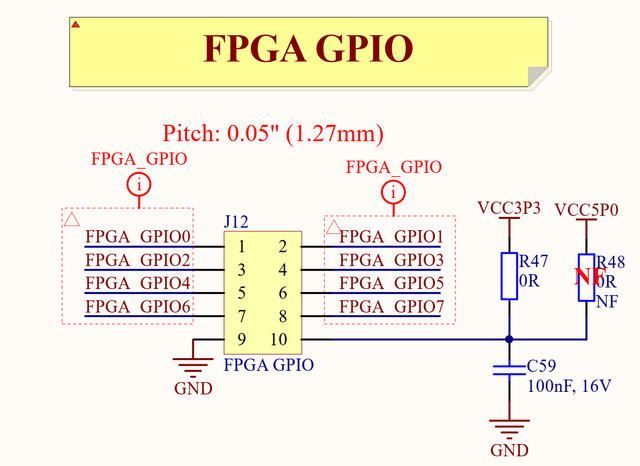
There are eight general purpose input/output pins from FPGA connected to FPGA GPIO header (J12). Schematic names and pin connections can be found in Table 4.
| Connector pin | Schematic signal name | FPGA pin | FPGA I/O standard | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FPGA_GPIO0 | M12 | 3.3V | |
| 2 | FPGA_GPIO1 | M10 | 3.3V | |
| 3 | FPGA_GPIO2 | N12 | 3.3V | |
| 4 | FPGA_GPIO3 | N10 | 3.3V | |
| 5 | FPGA_GPIO4 | M11 | 3.3V | |
| 6 | FPGA_GPIO5 | M9 | 3.3V | |
| 7 | FPGA_GPIO6 | N11 | 3.3V | |
| 8 | FPGA_GPIO7 | N9 | 3.3V | |
| 9 | GND | - | ||
| 10 | VCC | - | 3.3V or 5V selectable power rail. |
Voltage for pin 10 of J12 connector can be 3.3V (default) or 5V. To connect this pin to 5V power rail remove R47 and solder R48 resistors (see Figure 5).
Indication LEDs
Lime-GPSDO board comes with four dual color (red and green (RG)) indication LEDs. Most of LEDs are connected to FPGA and their function can be changed. Default LEDs functions and other information are listed in the table below.
| Board Reference | Schematic signal name | Board label | FPGA pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LED1 | FPGA_LED1_G | LED1 | A11 | GNSS lock and VCOCXO tune state: Solid RED – no GPS lock; Blinking RED – GPS is locked, 1s lowest accuracy tune state; Blinking RED/GREEN - GPS is locked, 10s accuracy tune state; Blinking GREEN - GPS is locked, 100s highest accuracy tune state. |
| FPGA_LED1_R | B11 | |||
| LED2 | FPGA_LED2_G | LED2 | A10 | |
| FPGA_LED2_R | B10 | |||
| LED3 | FPGA_LED3_G | LED3 | A8 | |
| FPGA_LED3_R | A9 | |||
| LED4 | - | LED4 VCC3P3 | - | Green LED indicates VCC3P3 power rail presence. Red LED is unused |
| - | - |