OpenAirInterface LTE: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 320: | Line 320: | ||
</nowiki> | </nowiki> | ||
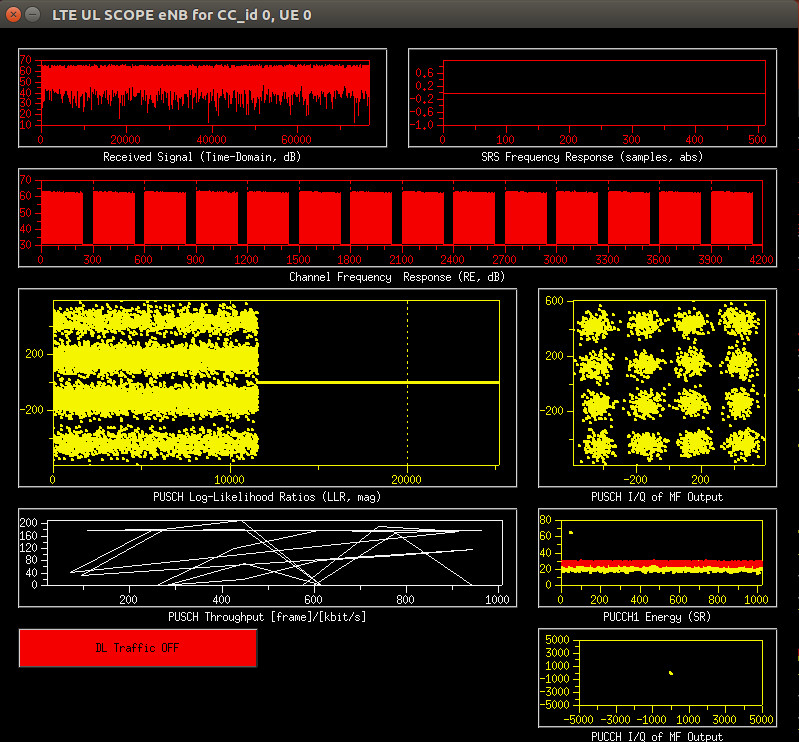
was partly solved by using the lte-softmodem -d switch Enable soft scope and L1 and L2 stats (Xforms), since it was built with the -x --xforms option, and | was partly solved by using the lte-softmodem -d switch Enable soft scope and L1 and L2 stats (Xforms), since it was built with the -x --xforms option, and | ||
partly by randomly moving the phone around and noticing there was a sweet spot where Firefox would download and install very fast. | partly by randomly moving the phone around and noticing there was a sweet spot where Firefox would download and install very fast.<br/><br/> | ||
Screenshot of a good connection<br/> | |||
[[File:OAI_LTE_8-09_Mbps_xforms.jpg]] | |||
Revision as of 19:34, 2 April 2018
Notes on a working OAI LTE project using a Samsung Galaxy S4 Mini, mainly pointers to build guides used and summary of obstacles encountered.
Result: Data transmission with an off the shelf cell phone up to 8Mbps (iperf) with very limited range using two antenna for tx and rx (proper duplexer project pending). That is, the phone must be experimentally positioned a less than a half meter from the LimeSDR and moved around until a good constellation display is found for best results.
Guides for installation:
[1]Main OAI page for setup with usrp device
[2]open-cells LimeSDR setup
[3]Recent (8/22/2017) all-in-one box build of OAI eNodeB and EPC components.
Hardware used:
Dell OptiPlex 9010 - quad core i7-3770 CPU @ 3.40GHz with USB3 support and hyperthreading turned off per OAI [4]recommendations
Bash script to turn off hyperthreading (/usr/local/bin/set-hyper-threading) from discussion [5].
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial - with low latency kernel
root@DellOptiPlex9010:~# uname -a Linux DellOptiPlex9010 4.13.0-36-lowlatency #40~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP PREEMPT Sat Feb 17 00:18:34 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
The latest available lowlatency kernel can be found with a search for the kernel module gpt.ko that will be needed to run the gateway module
# apt-file search gtp.ko | grep lowlatency linux-image-4.13.0-36-lowlatency: /lib/modules/4.13.0-36-lowlatency/kernel/drivers/net/gtp.ko # apt install linux-image-4.13.0-36-lowlatency
Beware if that particular kernel is no longer the primary boot image in grub.conf after an apt upgrate - or manually pick the kernel on startup, or change grub.conf to boot that particular image [6] - example /etc/default/grub:
GRUB_DEFAULT="Advanced options for Ubuntu>Ubuntu, with Linux 4.13.0-36-lowlatency"
So now we have a platform with i7-3770, no hyperthreading and lowlatency ready for OAI LTE.
And off we go:
~/src/oai$ git clone https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/oai/openairinterface5g.git Near 200MB cd openairinterface5g ~/src/oai/openairinterface5g$ source oaienv ~/src/oai/openairinterface5g$ ./build_oai -I --install-optional-packages <-- left this running in a screen, installs a bunch of pkgs -- hope it does not break my 2G stuff!
later ----
came home to find a question in the screen, about allowing non-root users to run wireshark packet capture - choose the not-recommended 'yes'
then fail on python ssl - had to fix with
python -m easy_install --upgrade pyOpenSSL
from [7]
re-run ./build_oai above and completed successfully
Next run
~/src/oai/openairinterface5g$ source oaienv Since I exited the screen with env set ~/src/oai/openairinterface5g$ ./cmake_targets/build_oai --eNB -w LMSSDR -c -C -x < ... > -- Build files have been written to: /home/chuck/src/oai/openairinterface5g/cmake_targets/lte_build_oai/build Compiling lte-softmodem Log file for compilation has been written to: /home/chuck/src/oai/openairinterface5g/cmake_targets/log/lte-softmodem.Rel14.txt lte-softmodem compiled Log file for compilation has been written to: /home/chuck/src/oai/openairinterface5g/cmake_targets/log/oai_lmssdrdevif.Rel14.txt oai_lmssdrdevif compiled liboai_device.so is linked to LMSSDR device library 10. Bypassing the Tests ...
More on build options:
A fellow in the discourse how-to-install-limesdr-on-openinterface-enodeb uses: ./build_oai -I --eNB -x -w LMSSDR
Add -x to enable xforms (soft scope), -w hardware EXMIMO, USRP, BLADERF, ETHERNET, LMSSDR, None (Default)
--eNB Makes the LTE softmodem -I Installs required packages such as LibXML, asn1.1 compiler, freediameter, ... <-- I did this seperately above
Above command had -c clean Erase all files to make a rebuild from start
-C clean-all Erase all files made by previous compilations, installations
The open-cells limesdr-installation used
./cmake_targets/build_oai -c -w LMSSDR --eNB --UE
for -c clean, -w hardware, --eNB and also --UE Makes the UE specific parts (ue_ip, usim, nvram) from the given configuration file -- default given config file is
/home/chuck/src/oai/openairinterface5g/openair3/NAS/TOOLS/ue_eurecom_test_sfr.conf
What you end up with after that build is:
targets/bin/liboai_device.so -> targets/bin/liboai_lmssdrdevif.so.Rel14 targets/bin/liboai_lmssdrdevif.so.Rel14 targets/bin/lte-softmodem.Rel14
and any custom LimeSDR tweaks like setting external clock reference or printing confirmation of antenna uses go in
targets/ARCH/LMSSDR/USERSPACE/LIB/lms_lib.cpp
plus it's just fun to read in itself with /usr/local/include/lime/LimeSuite.h open in another term. Of course rebuild lte-softmodem after any tweaks or experiments.
Do Download and Patch EPC from [8]
Install 3rd party software for EPC
source oaienv cd scripts ./build_hss -i Installing mysql - root user password: Pa$$word <intentionally including example password> installs freeDiameter - auth like RADIUS https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diameter_(protocol) installs apache, php -- for phpMyAdmin pick apache Configure database for phpmyadmin with dbconfig-common? Yes phpmyadmin password: Pa$$word
That was to install all the prereqs for hss - it will be built later, meanwhile prepare for
$ ./build_mme -i freeDiameter - no asn1c rev - no libgtpnl - yes hope this does not conflict with osmosgsn, ggsn GTP wireshark - done previously (non-root CAN run it)
$ ./build_spgw -i libftpnl - no this time
Next, actually compile them - just up-arrow and delete the -i
./build_hss '/home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/build/hss/build/oai_hss' -> '/usr/local/bin/oai_hss' oai_hss installed $ ls /usr/local/bin/oai_hss /usr/local/bin/oai_hss ./build_mme mme compiled '/home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/build/mme/build/mme' -> '/usr/local/bin/mme' mme installed auth_request compiled '/home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/build/mme/build/auth_request' -> '/usr/local/bin/auth_request' auth_request installed ./build_spgw spgw compiled '/home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/build/spgw/build/spgw' -> '/usr/local/bin/spgw' spgw installed
We are going to use this configuration:
HSS is on localhost: 127.0.0.1 eNB is on 127.0.0.10 MME is on 127.0.0.20 SPGW is on 127.0.0.30
I learned something about loopback lo interface here - you already have all 255^3 addresses available ready to use!
# ping 127.90.90.90 PING 127.90.90.90 (127.90.90.90) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 127.90.90.90: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.025 ms 64 bytes from 127.90.90.90: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.032 ms
So backup and edit the config file openairinterface5g/targets/PROJECTS/GENERIC-LTE-EPC/CONF/enb.band7.tm1.25PRB.lmssdr.conf to use this:
mme_ip_address = ( { ipv4 = "127.0.0.20"; -- rest the same
NETWORK_INTERFACES :
ENB_INTERFACE_NAME_FOR_S1_MME = "lo";
ENB_IPV4_ADDRESS_FOR_S1_MME = "127.0.0.10/8";
ENB_INTERFACE_NAME_FOR_S1U = "lo";
ENB_IPV4_ADDRESS_FOR_S1U = "127.0.0.10/8";
Here is a good discussion of the nodes and interfaces (S1-MME, S1-U, etc) to help visualize the interconnects [9]
Install This Configuration for EPC
in home ~ This uses the package d/l from [10]
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/oai sudo cp -rp ~/opencells-mods/config_epc/* /usr/local/etc/oai cd src/oai/openair-cn; source oaienv; cd scripts ./check_hss_s6a_certificate /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter hss.OpenAir5G.Alliance HSS S6A: Did not find valid certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter HSS S6A: generating new certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter... Creating HSS certificate for user 'hss.OpenAir5G.Alliance' ... Certificate is to be certified until Feb 24 18:51:15 2019 GMT (365 days) Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated /home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/scripts HSS S6A: Found valid certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter
So that cert is good for ONE YEAR Warning if still using it then
# less /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter/hss.cert.pem
Validity
Not Before: Feb 24 18:51:15 2018 GMT
'''Not After : Feb 24 18:51:15 2019''' GMT
./check_mme_s6a_certificate /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter mme.OpenAir5G.Alliance
File /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter/mme.cert.pem not found
MME S6A: Did not find valid certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter
MME S6A: generating new certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter...
Creating MME certificate for user 'mme.OpenAir5G.Alliance'
...
Certificate is to be certified until Feb 24 18:53:02 2019 GMT (365 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
/home/chuck/src/oai/openair-cn/scripts
MME S6A: Found valid certificate in /usr/local/etc/oai/freeDiameter
Then in /usr/local/etc/oai/spgw.conf change SGI to YOUR Internet facing interface:
PGW_INTERFACE_NAME_FOR_SGI = "enp0s31f6"; to PGW_INTERFACE_NAME_FOR_SGI = "eno1"; This is already set: PGW_MASQUERADE_SGI = "yes";
Warning: the config file /usr/local/etc/oai/hss.conf contains:
## HSS options #OPERATOR_key = "1006020f0a478bf6b699f15c062e42b3"; # OP key matching your database #OPERATOR_key = "11111111111111111111111111111111"; # OP key matching your database
The OPERATOR_key or 'OP' is an important part of the UE authentication, along with the key Ki and OPc. In fact, when the hss starts up is recalculates all the subscribers OPc from their key and this OPERATOR_key so they have to match what you use to write the OPc to the SIM card later. I picked a random OP (openssl rand -hex 16) and calculated the OPc from that with auchss.py [11].
Next discussion about MCC,MNC and headache getting an ebay special Galaxy S4Mini GT-I9195 [12] working on LTE with Sysmocom SIMS
While GSM is fairly easy to authenticate, you can use about any sim, LTE requires a SIM for which you know the Key Ki.
That means going ahead and buying the Sysmocom sysmoUSIM-SJS1 10 pack with the ADM keys.
They are very good and email the info for each card before you get them - the IMSI ICCID ACC PIN1 PUK1 PIN2 PUK2 Ki OPC ADM1 KIC1 KID1 and KIK1.
Another option might be piswords cards from Alibaba or ebay.
Will also need an affordable Scm Microsystems USB Smart Card Reader SCR3310V2.
The target UE, the SGS4Mini, that worked fine with osmocom gsm/gprs and had an Option for LTE bands
Band 3 - dl 1805 to 1880 Band 7 - dl 2620 to 2690 Band 8 - dl 925 to 960 Band 20 - dl 791 to 821
expecting to use band 7 which has a known working lte-softmodem configuration file for the LimeSDR (enb.band7.tm1.25PRB.lmssdr.conf). However on plugging in the SIM, the LTE
option disappeared, leaving only WCDMA UMTS and good ol' gsm. Much head scratching, searching and finding the Service Mode for the phone [13], finally tried changing the SIM MCC/MNC - mobile country code, mobile network code [14]. The Sysmocom SIMS come with 901/70 which looks like Satellite Network, unused network code. Tried the default OAI MCC/MNC 208/93 France, Unused network code, also UK, no luck. Tried a US code and got the LTE option but would not register. Finally discovered the IMEI of the phone contains a code for the country or origin [15], which in this case turns out to be Finland - tried a carrier there 244/91 and during tests with the easy to setup OpenLTE found the network "FI SONERA" finally. So the target UE likes 244/91 OK. Another helpful tool is the phone service mode mentioned above, *#0011# and then hit (menu) Back and then (menu) Key Input and enter Q0000 and wait. Then Select UMTS -> Debug Screen -> Phone Control -> Network Control -> Band Selection -> LTE Band and can pick 3,7,8,20 or * to narrow and speed up the network search.
For SIM programming this is a very useful page [16] that uses the strategy of copying a user that already exists in the example mysql oai_db 'users' table. They will also need to be put in the 'pdn' packet-data-network as detailed in step 2 of section 2.3 of [17]
The next obstacle was authentication, the OP issue mentioned above. A fail to connect issue was due to a confusion about OP and OPc programmed in the card.
/usr/local/etc/oai/hss.conf was setup with this as a random guess
## HSS options #OPERATOR_key = "1006020f0a478bf6b699f15c062e42b3"; # OP key matching your database OPERATOR_key = "11111111111111111111111111111111"; # OP key matching your database
That should give an OPc of:
OP: 11111111111111111111111111111111 Ki: 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 ~/src/sysmo-usim-tool$ ./auchss.py -o 11111111111111111111111111111111 -k 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 OP: 11111111111111111111111111111111 KI: 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 OPc: 327ed2b3a3437b08d5ad35875d222f29 <-- this
Matches db:
mysql> select hex(OPc) from users where imsi='244910000022771'; +----------------------------------+ | hex(OPc) | +----------------------------------+ | 327ED2B3A3437B08D5AD35875D222F29 | +----------------------------------+
but not the sim. I don't know how to get an OP to put in hss.conf from the existing OPc and Ki so reprogram the card with that OPc - use:
python pySim-prog.py --pcsc-device=0 --type="sysmoUSIM-SJS1" --mcc=244 --mnc=91 --imsi=244910000022771 --opc=327ED2B3A3437B08D5AD35875D222F29 --ki=39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 --iccid=8988211000000227713 --pin-adm=57942614 --acc=0002
--OR-- create a new OP
~$ openssl rand -hex 16 2f22315911b5ff00591be8b3898b4c09 ~/src/sysmo-usim-tool$ ./auchss.py -o 2f22315911b5ff00591be8b3898b4c09 -k 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 OP: 2f22315911b5ff00591be8b3898b4c09 KI: 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 OPc: 95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22 and program the card with: python pySim-prog.py --pcsc-device=0 --type="sysmoUSIM-SJS1" --mcc=244 --mnc=91 --imsi=244910000022771 --opc=95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22 --ki=39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 --iccid=8988211000000227713 --pin-adm=57942614 --acc=0002
To test that - update /usr/local/etc/oai/hss.conf with:
OPERATOR_key = "2f22315911b5ff00591be8b3898b4c09"; # random from openssl rand -hex 16
and startup
./run_hss
...
IMSI: 244910000022771Key: 39.86.0f.df.8d.53.1c.df.38.35.82.c4.ae.ef.a6.07.
OPc: 32.7e.d2.b3.a3.43.7b.08.d5.ad.35.87.5d.22.2f.29.
RijndaelKeySchedule: K 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607
Compute opc:
K: 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607
In: 2F22315911B5FF00591BE8B3898B4C09
Rinj: BAF9FDFD245CBD2392E371BBE936E22B
Out: 95DBCCA435E94223CBF8990860BDAE22
Query: UPDATE `users` SET `OPc`=UNHEX('95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22') WHERE `users`.`imsi`='244910000022771'
IMSI 244910000022771 Updated OPc 327ed2b3a3437b08d5ad35875d222f29 -> 95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22
...
correct! Just needs to program the SIM and it should connect OK this time :\
The options in pysim are:
-k KI, --ki=KI Ki (default is to randomize) -o OPC, --opc=OPC OPC (default is to randomize) --op=OP Set OP to derive OPC from OP and KI ~/src/pysim$ python pySim-prog.py --pcsc-device=0 --type="sysmoUSIM-SJS1" --mcc=244 --mnc=91 --imsi=244910000022771 --opc=95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22 --ki=39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 --iccid=8988211000000227713 --pin-adm=57942614 --acc=0002 Insert card now (or CTRL-C to cancel) Generated card parameters : > Name : Magic > SMSP : e1ffffffffffffffffffffffff0581005155f5ffffffffffff000000 > ICCID : 8988211000000227713 > MCC/MNC : 244/91 > IMSI : 244910000022771 > Ki : 39860FDF8D531CDF383582C4AEEFA607 > OPC : 95dbcca435e94223cbf8990860bdae22 > ACC : 0002 Programming ... Done !
That made progress indeed - at first could still not find the network - then fired up OpenLTE and let it fail on band20 a while - switched back to OAI band7 and soon as I changed the settings in service mode for LTE band selection it attached and got logs immediately!
[MAC][I][UL_failure_indication] [eNB 0][UE 0/80e6] Frame 620 subframeP 6 Signaling UL Failure for UE 0 on CC_id 0 (timer 0) [PHY][E]ERROR: Format 1A: rb_alloc (1ff) > RIV_max (144) [PHY][I][eNB 0][RAPROC] Frame 627 Terminating ra_proc for harq 4, UE 1 [MAC][I][rx_sdu] [eNB 627] Frame 6, Subframe 0 CC_id 0 MAC CE_LCID 27 (ce 0/3): CRNTI 80e6 (UE_id 0) in Msg3 [MAC][I][rx_sdu] [eNB 0] CC_id 0 MAC CE_LCID 29 : Received short BSR LCGID = 1 bsr = 33 [PHY][W][eNB 0, CC 0] frame 733, subframe 4, UE 0: ULSCH consecutive error count reached 20, triggering UL Failure [MAC][I][UL_failure_indication] [eNB 0][UE 0/80e6] Frame 733 subframeP 4 Signaling UL Failure for UE 0 on CC_id 0 (timer 0) [PHY][E]ERROR: Format 1A: rb_alloc (1ff) > RIV_max (144) [PHY][I][eNB 0][RAPROC] Frame 739 Terminating ra_proc for harq 4, UE 1 [MAC][I][rx_sdu] [eNB 739] Frame 6, Subframe 0 CC_id 0 MAC CE_LCID 27 (ce 0/3): CRNTI 80e6 (UE_id 0) in Msg3 [MAC][I][rx_sdu] [eNB 0] CC_id 0 MAC CE_LCID 30: Received long BSR LCGID0 = 0 LCGID1 = 0 LCGID2 = 0 LCGID3 = 0 [PHY][I]UE 0 : rnti 80e6 [MAC][I][eNB_dlsch_ulsch_scheduler] UE rnti 80e6 : in synch, PHR 40 dB CQI 10 [RRC][I]UE rnti 80e6 failure timer 0/20000 [PHY][W][eNB 0, CC 0] frame 733, subframe 8, UE 0: ULSCH consecutive error count reached 20, triggering UL Failure
tcpdump -i gtp0 gets this
17:41:56.461835 IP 172.16.0.10.47668 > ord30s25-in-f206.1e100.net.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:217, ack 1, win 229, options [nop,nop,TS val 43729 ecr 7671639], length 216 17:41:56.491983 IP ord30s25-in-f206.1e100.net.https > 172.16.0.10.47668: Flags [.], ack 217, win 170, options [nop,nop,TS val 7671748 ecr 43729], length 0
1e100 is a googol, the UE phoning home. it is pingable from the OAI host
# ping 172.16.0.10 PING 172.16.0.10 (172.16.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 172.16.0.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=73.9 ms 64 bytes from 172.16.0.10: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=61.2 ms
The last puzzle piece with the lousy bursty throughput and those log errors:
[PHY][W][eNB 0, CC 0] frame 733, subframe 4, UE 0: ULSCH consecutive error count reached 20, triggering UL Failure [MAC][I][UL_failure_indication] [eNB 0][UE 0/80e6] Frame 733 subframeP 4 Signaling UL Failure for UE 0 on CC_id 0 (timer 0) [PHY][E]ERROR: Format 1A: rb_alloc (1ff) > RIV_max (144)
was partly solved by using the lte-softmodem -d switch Enable soft scope and L1 and L2 stats (Xforms), since it was built with the -x --xforms option, and
partly by randomly moving the phone around and noticing there was a sweet spot where Firefox would download and install very fast.
Screenshot of a good connection